Deploy LLMs on AWS 72% Cheaper in Production
Deploy open-source LLMs on AWS with confidence using the industry’s broadest GPU portfolio and managed services like SageMaker. AWS supports models at any scale while cutting costs up to 72% through Reserved Instances, Spot capacity, and Inferentia2 optimization.

TLDR;
- Save up to 72% on AWS LLM deployments using Reserved Instances and Spot capacity
- Inferentia2 chips cut inference costs 40% compared to equivalent GPU instances
- Four deployment paths: SageMaker (managed), EC2 (full control), ECS (containers), Lambda (serverless)
- Start with SageMaker for simplicity — scale to EC2 when you need direct hardware access
Deploy open source LLMs on AWS with confidence. AWS holds 34% of the cloud AI infrastructure market with 18 specialized GPU instances and purpose-built inference hardware. This guide shows you how to cut costs while maintaining enterprise-grade performance.
Why AWS Leads Enterprise LLM Deployment
AWS offers the broadest GPU instance portfolio in the industry. P5 instances provide NVIDIA H100 GPUs with 640GB of HBM3 memory. G5 instances deliver A10G GPUs for balanced workloads. Inferentia2 chips cut inference costs by 40%.
SageMaker manages infrastructure automatically and integrates with over 200 AWS services. Reserved Instances save up to 72% compared to on-demand pricing. Spot instances cost 40–70% less for fault-tolerant workloads.
Understanding AWS LLM Deployment Options
You have four main paths to deploy LLMs on AWS. Each serves different needs.
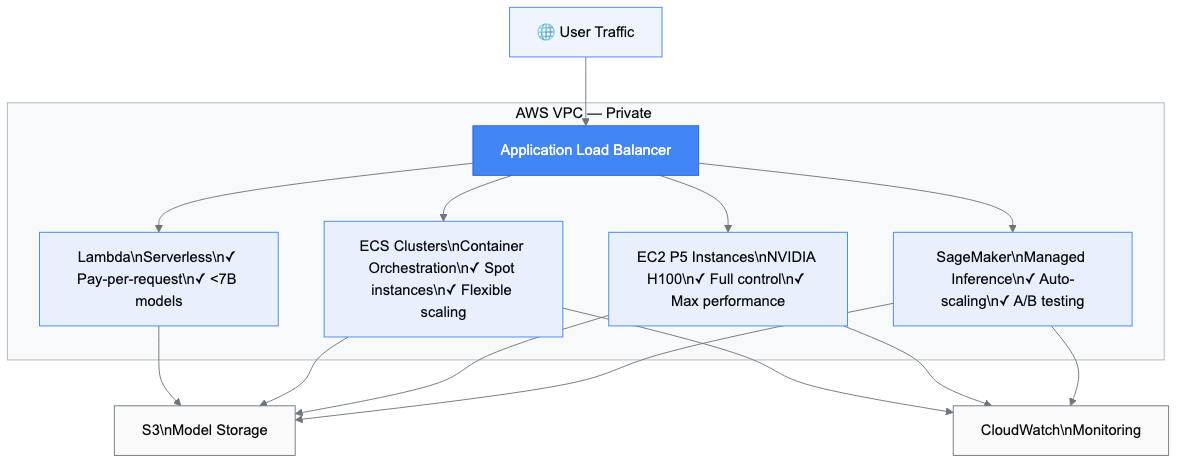
SageMaker for Managed Deployment
SageMaker takes care of the infrastructure. Real-time endpoints auto-scale based on traffic. Serverless inference charges $0.20 per invocation plus $0.0003 per GB-second. The Model Registry tracks versions and manages approvals, preventing accidental production deployments.
EC2 for Maximum Control
EC2 gives you direct hardware access. P5 instances pack 8 NVIDIA H100 GPUs with 640GB of HBM3 memory. G5 instances offer better price-performance with 24GB VRAM starting at $1.006/hour. Inf2 instances run Inferentia2 chips purpose-built for inference, delivering 40% cost reduction. The tradeoff: you manage the infrastructure, drivers, and monitoring yourself.
ECS for Container Orchestration
Amazon ECS runs containerized LLM workloads with ECS-optimized AMIs that include NVIDIA drivers pre-installed. Spot instances integrate seamlessly, saving 40–70% on compute. ECS automatically replaces interrupted instances via Spot Fleet.
Lambda for Lightweight Models
Lambda runs event-driven inference scaling from zero to thousands of concurrent executions. Constraints apply: 15-minute runtime, 10GB memory, 10GB image size — restricting this path to models under 7B parameters. Cold starts add 5–10 seconds of latency.
Cost Optimization Strategies That Work
Cost optimization makes or breaks LLM deployments. Here's how to cut your AWS bill significantly.
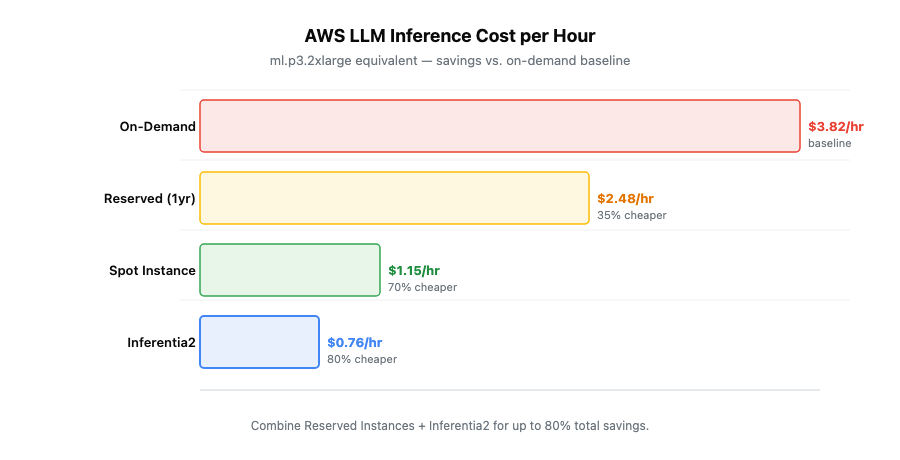
Reserved Instances and Savings Plans
Reserved Instances offer 42% savings on 1-year terms and 72% on 3-year terms over on-demand pricing. Convertible RIs let you change instance types while keeping your discount. SageMaker Savings Plans target ML workloads specifically: 40% on 1-year, 64% on 3-year commitments.
Spot Instance Strategies
Spot instances cost 40–70% less than on-demand. AWS can reclaim them with 2 minutes notice — handle this with checkpointing every few minutes. SageMaker Managed Spot Training saves up to 90% on training costs and handles checkpointing automatically.
Inferentia2 Optimization
Inferentia2 chips deliver 40% cost reduction for inference. The Neuron SDK compiles models automatically for Inferentia hardware — PyTorch and TensorFlow models work without major rewrites. Dynamic batching increases throughput. Model caching eliminates cold starts.
Multi-Region Deployment for Global Scale
Deploy across AWS regions to reduce latency and improve availability.
Architecture Patterns
Active-Active runs full deployments in multiple regions with Route 53 latency-based routing directing traffic automatically. CloudFront caches responses at 400+ edge locations. Warm Standby maintains scaled-down secondary infrastructure with RTO under 30 minutes.
Data Synchronization
S3 Cross-Region Replication copies model artifacts automatically. DynamoDB Global Tables synchronize application state with sub-second replication. Aurora Global Database handles multi-region read-write with up to five read replicas globally.
Security and Compliance Framework
Enterprise deployments require robust security. AWS provides the tools built in.
Network Isolation
Deploy SageMaker endpoints in private subnets — they never touch the public internet. Security groups act as stateful firewalls. PrivateLink creates private connections to AWS services, keeping all traffic within the AWS network.
Encryption and Access Management
TLS 1.2+ encrypts all API communications. S3 default encryption secures model artifacts at rest. AWS KMS manages keys with customer-managed options for full regulatory control. Apply the principle of least privilege — grant only necessary permissions. AWS Secrets Manager stores API keys with automatic rotation.
Monitoring and Observability
Production deployments need consistent monitoring to catch problems before users do.
CloudWatch Integration
CloudWatch collects metrics automatically: model invocations per minute, P95 latency, 4xx and 5xx error rates. Set alarms on threshold violations to get notified before users experience problems. Log Insights provides SQL-like queries for analysis across all service logs.
SageMaker Model Monitor and Distributed Tracing
Model Monitor detects drift in production by comparing live traffic against training baselines — catching schema changes, shifting feature distributions, and accuracy degradation. AWS X-Ray traces requests end-to-end showing exactly where latency occurs. Service maps visualize dependencies and anomaly detection highlights performance issues automatically.
MLOps and CI/CD Integration
Automate deployment to maintain velocity without sacrificing reliability.
SageMaker Pipelines defines ML workflows as directed acyclic graphs covering data processing, training, evaluation, and deployment. Conditional execution adds business logic — skip retraining if accuracy meets thresholds. The Model Registry versions every artifact with approval workflows preventing premature production deployments. CloudFormation and CDK manage infrastructure as code with version control built in.
Model-Specific Deployment Examples
Different models need different approaches. Here are production-tested configurations.
Qwen 2.5 on SageMaker
Use g5.2xlarge instances for the 7B model — 48GB VRAM handles batched requests efficiently. For the 72B model, step up to p5.48xlarge with 640GB of HBM3 memory. Apply 4-bit quantization to cut memory requirements in half with minimal quality degradation.
DeepSeek V3 on ECS with Auto-Scaling
DeepSeek V3's 671B MoE architecture only loads active experts into GPU memory. Deploy on ECS with g5.12xlarge instances (96GB VRAM). Configure target tracking scaling at 70% GPU utilization. Use Application Load Balancer with connection draining so in-flight requests complete before instances terminate.
Llama 3.3 70B on EC2 P5
Launch p5.48xlarge with 8 H100 GPUs and tensor parallelism via Ray Serve. Enable EFA (Elastic Fabric Adapter) for multi-node deployments — 3200 Gbps networking minimizes communication overhead. Reserve P5 capacity in advance; these instances face high demand.
Best Practices for Production
Start small and scale based on actual metrics. Run load tests before go-live measuring throughput, latency, and cost at different concurrency levels. Define custom health endpoints verifying model functionality and latency thresholds.
Deploy across multiple availability zones. Implement circuit breakers to prevent cascading failures. Benchmark batch sizes for your workload — larger batches increase throughput but add latency, so find the right balance before production.
Getting Started: Your First Deployment
Ready to deploy? Follow this four-week roadmap.
- Week 1 — Setup and Planning. Create an AWS account and set up billing alerts immediately. Define requirements: which model, expected query volume, latency tolerance, and budget. Choose your deployment path.
- Week 2 — Proof of Concept. Deploy a small model on SageMaker using a pre-trained model from Hugging Face. Send test requests and measure actual latency and cost. Confirm the infrastructure works before tackling larger deployments.
- Week 3 — Production Infrastructure. Create a VPC with private subnets. Configure security groups restrictively. Deploy your model to real-time endpoints. Set up CloudWatch dashboards and alerts.
- Week 4 — Optimization and Monitoring. Check GPU utilization hourly. Review CloudWatch metrics daily. Calculate actual costs versus budget. Purchase Reserved Instances for predictable workloads.
Conclusion
AWS provides the most mature platform for enterprise LLM deployments — 34% market share, 18 specialized GPU instance types, and purpose-built inference hardware that no other cloud matches today.
Cost optimization opportunities are real: 72% savings through Reserved Instances, 40–70% through Spot capacity, and 40% through Inferentia2. Most organizations reach positive ROI within six months.
Security and compliance features meet enterprise requirements out of the box. VPC isolation, KMS encryption, and IAM least-privilege policies integrate without custom tooling.
Start with SageMaker for managed simplicity. Scale to EC2 when you need direct hardware access. Monitor constantly and optimize continuously. If you want expert guidance on your AWS LLM architecture, EaseCloud's AWS consulting team has deployed production LLM infrastructure across 40+ enterprises.
Frequently Asked Questions
What's the most cost-effective way to deploy LLMs on AWS?
For intermittent traffic, use SageMaker Serverless Inference — pay only per request at $0.20/invocation. For steady traffic, combine Reserved Instances (42% savings on 1-year) with Spot capacity. This typically cuts costs 60–70% versus on-demand.
Should I use SageMaker or EC2 for production LLM deployment?
Use SageMaker unless you need custom GPU configurations, direct hardware access, or specialized networking. Most teams benefit from managed auto-scaling and built-in monitoring. Switch to EC2 only when you hit SageMaker's limits.
How do I deploy models larger than 100B parameters?
P5 instances with 8 H100 GPUs handle up to 200B parameters. For larger models, use tensor parallelism across multiple P5 instances. Apply 4-bit quantization to halve memory requirements with under 5% quality loss.
How can I reduce inference costs by 40% or more?
Switch to Inferentia2 instances (40% cheaper than GPU equivalents), purchase 1-year Reserved Instances (42% savings), and enable dynamic batching. Combining all three cuts inference spend by 60–80%.