Track Production LLM Metrics with CloudWatch
Monitor production LLMs on AWS with CloudWatch to track latency, errors, and GPU health, build dashboards, set alerts, analyze logs, and use X-Ray tracing to detect issues early and maintain reliable, SLA-compliant inference at scale.
TLDR;
- Track P50, P95, P99 latency and error rates with automatic SageMaker metric collection
- Custom GPU metrics monitor utilization, memory, temperature, and power draw
- Configure alarms at 80% of SLA thresholds for proactive warning before user impact
- X-Ray distributed tracing pinpoints bottlenecks across tokenization, inference, and post-processing
Monitor LLM deployments with CloudWatch for reliability and performance. This guide shows you how to track metrics, set up alerts, and debug issues in production.
Production LLMs fail in subtle ways that only comprehensive monitoring can detect. Latency gradually increases, error rates spike unexpectedly, and GPU memory leaks develop slowly over time. Without proper monitoring infrastructure, you discover these issues when users complain rather than through proactive alerts. This guide provides complete CloudWatch monitoring setup for AWS LLM deployments, covering automatic metric collection from SageMaker and EC2, custom application metrics for business-specific tracking, and automated alerting through SNS. You'll learn how to create production dashboards visualizing performance across all endpoints, configure alarms for high latency and error rates, aggregate logs from distributed systems, and use X-Ray for distributed tracing. Implementation includes GPU monitoring with custom metrics, Log Insights queries for pattern detection, and cost optimization strategies to minimize monitoring expenses. Whether you're running SageMaker endpoints, EC2 GPU instances, or ECS containers, this tutorial delivers production-tested monitoring patterns ensuring reliability, performance visibility, and SLA compliance for enterprise LLM deployments.
CloudWatch Capabilities
Key features:
- Automatic metric collection from SageMaker/EC2
- Custom metrics for application-specific tracking
- Automated alerting via SNS
- Integration with X-Ray for distributed tracing
- Log aggregation and analysis
- Dashboards for visualization
Essential Metrics to Track
Monitor these metrics for healthy LLM deployments.
SageMaker Endpoint Metrics
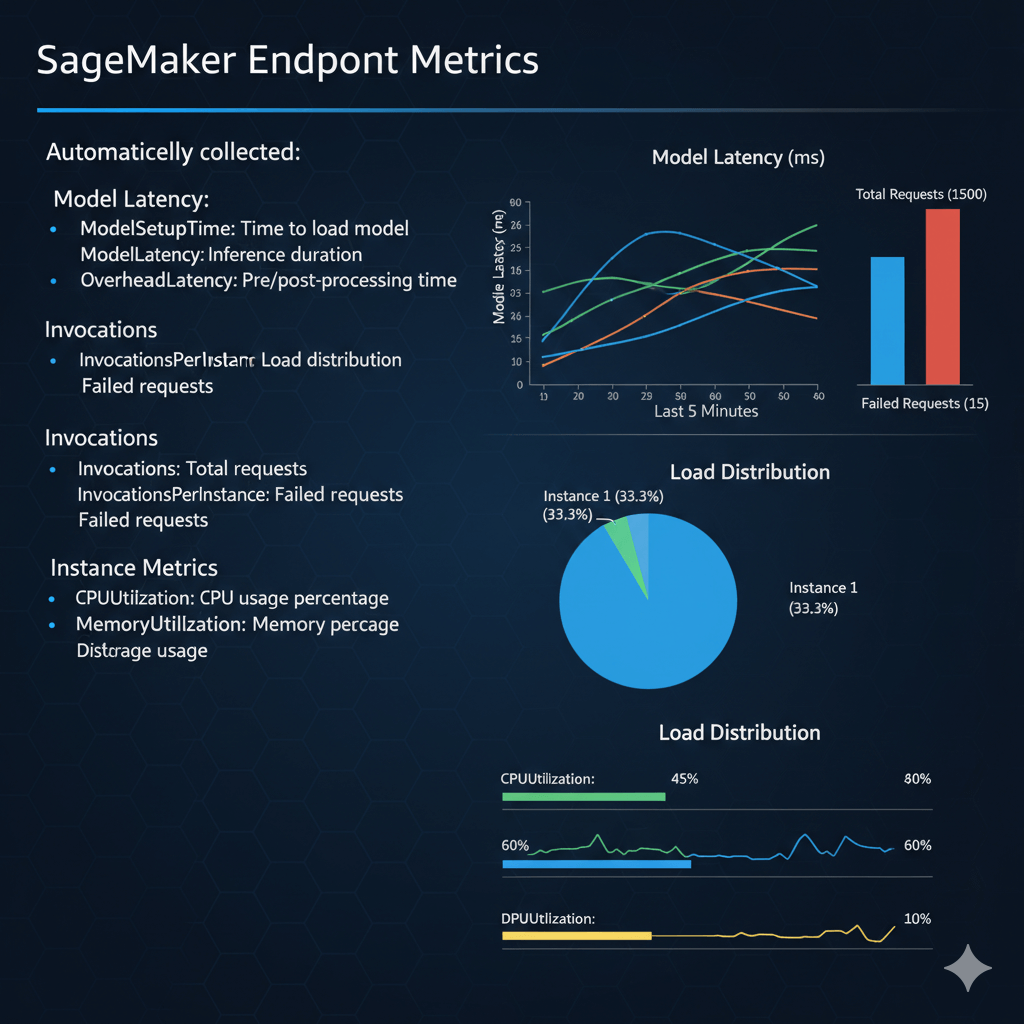
Automatically collected:
Model Latency:
- ModelSetupTime: Time to load model
- ModelLatency: Inference duration
- OverheadLatency: Pre/post-processing time
Invocations:
- Invocations: Total requests
- InvocationsPerInstance: Load distribution
- ModelInvocationErrors: Failed requests
Instance Metrics:
- CPUUtilization: CPU usage percentage
- MemoryUtilization: Memory usage percentage
- DiskUtilization: Storage usage
Custom Application Metrics
Track business-specific metrics:
from datetime import datetime
cloudwatch = boto3.client('cloudwatch')
def publish_custom_metrics(
tokens_generated,
prompt_length,
response_quality_score
):
cloudwatch.put_metric_data(
Namespace='LLM/Production',
MetricData=[
{
'MetricName': 'TokensGenerated',
'Value': tokens_generated,
'Unit': 'Count',
'Timestamp': datetime.utcnow(),
'Dimensions': [
{'Name': 'Model', 'Value': 'llama-70b'},
{'Name': 'Environment', 'Value': 'production'}
]
},
{
'MetricName': 'PromptLength',
'Value': prompt_length,
'Unit': 'Count',
'StorageResolution': 1 # High-resolution (1-second)
},
{
'MetricName': 'QualityScore',
'Value': response_quality_score,
'Unit': 'None',
'StatisticValues': {
'SampleCount': 1,
'Sum': response_quality_score,
'Minimum': response_quality_score,
'Maximum': response_quality_score
}
}
]
)
GPU Metrics (EC2)
Monitor GPU utilization:
import boto3
def collect_gpu_metrics():
result = subprocess.run([
'nvidia-smi',
'--query-gpu=utilization.gpu,memory.used,temperature.gpu,power.draw',
'--format=csv,noheader,nounits'
], capture_output=True, text=True)
cloudwatch = boto3.client('cloudwatch')
for idx, line in enumerate(result.stdout.strip().split('\n')):
gpu_util, mem_used, temp, power = map(float, line.split(', '))
cloudwatch.put_metric_data(
Namespace='GPU/Metrics',
MetricData=[
{
'MetricName': 'GPUUtilization',
'Value': gpu_util,
'Unit': 'Percent',
'Dimensions': [
{'Name': 'InstanceId', 'Value': instance_id},
{'Name': 'GPUIndex', 'Value': str(idx)}
]
},
{
'MetricName': 'GPUMemoryUsed',
'Value': mem_used,
'Unit': 'Megabytes'
},
{
'MetricName': 'GPUTemperature',
'Value': temp,
'Unit': 'None'
},
{
'MetricName': 'PowerDraw',
'Value': power,
'Unit': 'None'
}
]
)
# Run every 60 seconds
import schedule
schedule.every(60).seconds.do(collect_gpu_metrics)
Creating Dashboards
Visualize metrics for quick insights.
Production Dashboard
import json
cloudwatch = boto3.client('cloudwatch')
dashboard_config = {
"widgets": [
{
"type": "metric",
"x": 0,
"y": 0,
"width": 12,
"height": 6,
"properties": {
"metrics": [
["AWS/SageMaker", "ModelLatency", {"stat": "Average"}],
["...", {"stat": "p95"}],
["...", {"stat": "p99"}]
],
"period": 300,
"stat": "Average",
"region": "us-east-1",
"title": "Model Latency (ms)",
"yAxis": {
"left": {"min": 0}
}
}
},
{
"type": "metric",
"x": 12,
"y": 0,
"width": 12,
"height": 6,
"properties": {
"metrics": [
["AWS/SageMaker", "Invocations", {"stat": "Sum"}],
[".", "ModelInvocationErrors", {"stat": "Sum"}]
],
"period": 300,
"stat": "Sum",
"region": "us-east-1",
"title": "Requests & Errors"
}
},
{
"type": "metric",
"x": 0,
"y": 6,
"width": 24,
"height": 6,
"properties": {
"metrics": [
["GPU/Metrics", "GPUUtilization", {"stat": "Average"}],
[".", "GPUMemoryUsed", {"yAxis": "right"}]
],
"period": 60,
"stat": "Average",
"region": "us-east-1",
"title": "GPU Utilization",
"yAxis": {
"left": {"label": "Utilization %", "min": 0, "max": 100},
"right": {"label": "Memory MB"}
}
}
}
]
}
cloudwatch.put_dashboard(
DashboardName='LLMProduction',
DashboardBody=json.dumps(dashboard_config)
)
Setting Up Alerts
Automated alerts prevent outages.
High Latency Alert
AlarmName='LLM-High-Latency',
ComparisonOperator='GreaterThanThreshold',
EvaluationPeriods=2,
MetricName='ModelLatency',
Namespace='AWS/SageMaker',
Period=300, # 5 minutes
Statistic='Average',
Threshold=1000.0, # 1 second
ActionsEnabled=True,
AlarmActions=[
'arn:aws:sns:us-east-1:account:ops-alerts'
],
AlarmDescription='Alert when model latency exceeds 1 second',
Dimensions=[
{'Name': 'EndpointName', 'Value': 'llama-endpoint'},
{'Name': 'VariantName', 'Value': 'AllTraffic'}
],
TreatMissingData='notBreaching'
)
Error Rate Alert
AlarmName='LLM-High-Error-Rate',
ComparisonOperator='GreaterThanThreshold',
EvaluationPeriods=1,
Metrics=[
{
'Id': 'error_rate',
'Expression': '(errors / invocations) * 100',
'Label': 'Error Rate %'
},
{
'Id': 'errors',
'MetricStat': {
'Metric': {
'Namespace': 'AWS/SageMaker',
'MetricName': 'ModelInvocationErrors',
'Dimensions': [
{'Name': 'EndpointName', 'Value': 'llama-endpoint'}
]
},
'Period': 300,
'Stat': 'Sum'
},
'ReturnData': False
},
{
'Id': 'invocations',
'MetricStat': {
'Metric': {
'Namespace': 'AWS/SageMaker',
'MetricName': 'Invocations',
'Dimensions': [
{'Name': 'EndpointName', 'Value': 'llama-endpoint'}
]
},
'Period': 300,
'Stat': 'Sum'
},
'ReturnData': False
}
],
Threshold=5.0, # 5% error rate
AlarmActions=['arn:aws:sns:us-east-1:account:critical-alerts']
)
GPU Temperature Alert
AlarmName='GPU-High-Temperature',
ComparisonOperator='GreaterThanThreshold',
EvaluationPeriods=3,
MetricName='GPUTemperature',
Namespace='GPU/Metrics',
Period=60,
Statistic='Average',
Threshold=80.0, # 80°C
ActionsEnabled=True,
AlarmActions=['arn:aws:sns:us-east-1:account:hardware-alerts'],
AlarmDescription='Alert when GPU temperature exceeds 80°C'
)
Log Aggregation and Analysis
Centralize logs for debugging.
CloudWatch Logs Integration
import boto3
from watchtower import CloudWatchLogHandler
# Configure CloudWatch Logs handler
cloudwatch_handler = CloudWatchLogHandler(
log_group='/aws/llm/production',
stream_name='inference-server',
send_interval=10, # Send every 10 seconds
create_log_group=True
)
# Setup logging
logger = logging.getLogger('llm-inference')
logger.addHandler(cloudwatch_handler)
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
# Log inference requests
def log_inference(prompt, response, latency):
logger.info('Inference completed', extra={
'prompt_length': len(prompt),
'response_length': len(response),
'latency_ms': latency,
'timestamp': datetime.utcnow().isoformat()
})
Log Insights Queries
Find patterns in logs:
fields @timestamp, latency_ms, prompt_length
| filter latency_ms > 1000
| sort latency_ms desc
| limit 20
-- Error analysis
fields @timestamp, @message
| filter @message like /error|exception/
| stats count() by bin(5m)
-- Token usage analysis
fields @timestamp, prompt_length, response_length
| stats avg(prompt_length), avg(response_length), sum(response_length) by bin(1h)
Automated Log Analysis
Create insights from logs:
# Query logs
response = logs.start_query(
logGroupName='/aws/llm/production',
startTime=int((datetime.now() - timedelta(hours=1)).timestamp()),
endTime=int(datetime.now().timestamp()),
queryString='''
fields @timestamp, latency_ms
| filter latency_ms > 500
| stats count() as slow_requests, avg(latency_ms) as avg_latency
'''
)
query_id = response['queryId']
# Wait for results
import time
while True:
result = logs.get_query_results(queryId=query_id)
if result['status'] == 'Complete':
print(result['results'])
break
time.sleep(1)
X-Ray Distributed Tracing
Debug complex request flows.
Enable X-Ray Tracing
from aws_xray_sdk.ext.flask.middleware import XRayMiddleware
app = Flask(__name__)
XRayMiddleware(app, xray_recorder)
@app.route('/generate')
@xray_recorder.capture('generate_text')
def generate():
# Trace subsegments
with xray_recorder.in_subsegment('tokenize') as subsegment:
tokens = tokenizer(prompt)
subsegment.put_metadata('token_count', len(tokens))
with xray_recorder.in_subsegment('inference') as subsegment:
output = model.generate(tokens)
subsegment.put_annotation('model', 'llama-70b')
return output
Conclusion
CloudWatch monitoring provides comprehensive visibility into production LLM deployments, enabling proactive issue detection before users experience problems. Automated metric collection from SageMaker and EC2 combined with custom application metrics delivers complete performance tracking. Configured alarms for latency, error rates, and GPU utilization ensure immediate notification of anomalies. CloudWatch Logs aggregation centralizes debugging information, while Log Insights queries reveal patterns in request failures and performance degradation. X-Ray distributed tracing pinpoints bottlenecks across complex request flows. Production dashboards visualize metrics across all endpoints, enabling quick assessment of system health. Cost optimization through metric resolution tuning, log retention policies, and metric math expressions keeps monitoring expenses minimal. For enterprise LLM deployments requiring reliability, performance visibility, and SLA compliance, CloudWatch provides the essential monitoring foundation. Start with essential metrics like P95 latency and error rates, configure alerts at 80% of SLA thresholds for warnings, and expand monitoring as your deployment scales to maintain production excellence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What metrics should I prioritize for LLM inference monitoring?
Focus on these critical metrics in priority order: (1) Request latency percentiles (P50, P95, P99) - alerts when P95 exceeds 2x baseline indicate capacity issues; (2) Throughput (requests/second and tokens/second) - sudden drops signal problems; (3) Error rate percentage - spike above 1% requires immediate investigation; (4) GPU utilization - sustained <60% suggests over-provisioning, >95% indicates under-capacity; (5) Queue depth - growing queues predict future latency problems. Set CloudWatch alarms: P95 latency >2x baseline (warning) or >5x baseline (critical), error rate >1% (critical), GPU memory >90% (warning). Monitor these via CloudWatch dashboards with 1-minute granularity for production endpoints. Secondary metrics include model loading time, cache hit rates, and cold start frequency for auto-scaling deployments.
How do I troubleshoot high latency spikes in CloudWatch?
Correlate latency spikes with other metrics to identify root cause. Check GPU utilization during spike - if maxed at 100%, add instances or upgrade to larger GPU types. Review error logs in CloudWatch Logs Insights during spike time window - OOM errors indicate memory exhaustion, timeout errors suggest model overload. Analyze request patterns - sudden traffic surge may overwhelm queue, check concurrent requests metric. Use X-Ray traces to pinpoint bottlenecks in request path (tokenization, inference, post-processing). Create correlation rule in CloudWatch to automatically link high latency with: increased request rate, GPU throttling events, or instance health checks failing. Enable detailed monitoring (1-minute intervals) versus standard (5-minute) to catch transient issues. For persistent problems, enable SageMaker Debugger to profile GPU kernel execution and identify slow operations.
Can I integrate CloudWatch with external monitoring tools like Datadog?
Yes, CloudWatch integrates with most monitoring platforms via AWS integrations or CloudWatch metric streams. For Datadog, use the official AWS integration which polls CloudWatch APIs every 5–10 minutes for metrics, or configure CloudWatch Metric Streams for real-time 60-second delivery via Kinesis Firehose to Datadog (lower latency, higher cost). For Prometheus/Grafana, use CloudWatch Exporter to scrape metrics and expose Prometheus format, or AWS Distro for OpenTelemetry (ADOT) for native export. New Relic, Splunk, and Elastic offer similar CloudWatch connectors. Consider costs—metric streams at $0.003/metric update can add $500–2000/month for busy inference endpoints with 100+ metrics, which is why many teams engage AWS cost optimization consulting to balance observability depth with spend. For cost-sensitive deployments, stick with CloudWatch native dashboards and use integrations only for critical metrics requiring correlation with non-AWS data sources or consolidated multi-cloud views.