Serve Models on GCP with 91% Cost Savings
Deploy open-source LLMs on GCP using Vertex AI, TPUs, Cloud Run, and GKE to reduce ops overhead and cut costs up to 91%, with serverless scaling, high-performance ML infrastructure, and production-ready deployment patterns.

TLDR;
- Save up to 91% with 3-year Committed Use Discounts and spend-based commitments
- TPU v5p delivers 2.7x faster inference than previous generations for large models
- Cloud Run scales to zero automatically for intermittent workloads with sub-1-second cold starts
- 100% renewable energy operations support ESG objectives while reducing costs
Deploy open source LLMs on Google Cloud Platform with TPU optimization and serverless scaling. GCP offers managed ML services that reduce operational overhead while cutting costs up to 91%. This guide covers Vertex AI, Cloud Run, and GKE deployment strategies for production workloads.
Why GCP Leads ML Infrastructure
Google Cloud Platform holds 22% of the cloud ML market. The platform invented the Transformer architecture, created TensorFlow, and developed TPUs specifically for ML workloads.
Vertex AI provides a unified ML platform. Train models, deploy endpoints, and monitor performance from one interface. TPU v5p delivers 1.4 petaflops of compute per pod with 2.7x faster inference than previous generations.
Cost optimization options include Committed Use Discounts saving up to 91% for 3-year commitments and Preemptible VMs cutting batch processing costs by 80%. GCP runs on 100% renewable energy with carbon-neutral operations meeting ESG requirements.
Understanding GCP ML Architecture
GCP offers three primary deployment paths. Each serves different needs.
Vertex AI for Managed ML
Vertex AI handles your ML infrastructure end-to-end.
Prediction endpoints deploy models with a few clicks. Auto-scaling adjusts capacity based on demand. You pay only for compute time used.
Model Registry versions every model. Track experiments. Compare performance. Roll back when needed. Full lineage from training data to deployed model.
Feature Store centralizes feature engineering. Share features across teams. Reduce duplicated work. Ensure consistency between training and serving.
Explainable AI shows why models make predictions. Required for regulated industries. Builds trust with stakeholders. Identifies bias before it causes problems.
BigQuery ML integration trains models where your data lives. No data movement required. Query your models with SQL. Perfect for analysts without Python skills.
Cloud Run for Serverless Deployment
Cloud Run deploys containerized workloads serverlessly.
You pay per request. Idle time costs nothing. Perfect for intermittent inference workloads that don't justify always-on infrastructure.
Scaling happens automatically. From zero to thousands of instances in seconds. No configuration required.
CPU and memory allocation flexes up to 8 vCPUs and 32GB per container. Enough for most models under 7B parameters after quantization.
Cold starts improved dramatically in 2024. Startup time under 1 second for optimized containers. Second generation execution environment reduces latency.
Custom domains and SSL certificates work out of the box. Cloud Run generates certificates automatically. Your API runs on your domain immediately.
apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: llm-inference
spec:
template:
metadata:
annotations:
autoscaling.knative.dev/minScale: "0"
autoscaling.knative.dev/maxScale: "100"
spec:
containers:
- image: gcr.io/project/llm-model:latest
resources:
limits:
cpu: "4"
memory: "16Gi"
env:
- name: MODEL_PATH
value: "gs://bucket/models/latest"
GKE for Production Scale
Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) runs production ML workloads at enterprise scale.
Autopilot mode manages cluster operations automatically. Node sizing. Upgrades. Security patches. You focus on workloads, not infrastructure.
GPU node pools support NVIDIA A100, V100, and T4 accelerators. Right-size based on your model requirements and budget.
Horizontal Pod Autoscaling responds to load. Vertical Pod Autoscaling optimizes resource requests. Cluster autoscaling adjusts node count. All work together seamlessly.
Workload Identity binds Kubernetes service accounts to Google Cloud IAM. Your pods access Cloud Storage and Vertex AI without storing credentials.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: model-server
spec:
replicas: 3
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: inference
image: gcr.io/project/model:v1
resources:
limits:
nvidia.com/gpu: 1
memory: "24Gi"
requests:
cpu: "4"
memory: "16Gi"
nodeSelector:
cloud.google.com/gke-accelerator: nvidia-tesla-a100
TPU Optimization for Maximum Performance
TPUs deliver Google's best price-performance for ML workloads.
TPU v5p Architecture
TPU v5p pods contain thousands of TPU cores. They're designed specifically for large language models.
Each v5p chip delivers 459 teraflops of bfloat16 performance. Pods scale to 8,960 chips. That's over 4 exaflops of compute.
High-bandwidth inter-chip networking eliminates communication bottlenecks. 4.8 Tbps per chip bidirectional bandwidth. Models distributed across TPUs run like single-device workloads.
Water cooling keeps TPUs running efficiently. Power usage drops 20% compared to air cooling. Data center costs decrease.
Optimizing Models for TPU
TPUs perform best with large batch processing. Optimize your workloads accordingly.
Use XLA (Accelerated Linear Algebra) compilation. It optimizes TensorFlow and JAX graphs specifically for TPU architecture. Performance improves 2-3x versus unoptimized code.
Batch requests aggressively. TPUs achieve maximum efficiency at batch sizes of 128-1024. Smaller batches waste compute capacity.
Use bfloat16 precision. TPUs process bfloat16 much faster than float32. Model quality degradation is minimal for most workloads.
# Configure TPU
resolver = tf.distribute.cluster_resolver.TPUClusterResolver()
tf.config.experimental_connect_to_cluster(resolver)
tf.tpu.experimental.initialize_tpu_system(resolver)
strategy = tf.distribute.TPUStrategy(resolver)
# Load model on TPU
with strategy.scope():
model = tf.keras.models.load_model('gs://bucket/model')
model.compile(
optimizer='adam',
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy']
)
# Run inference with large batch
predictions = model.predict(data, batch_size=512)
When to Choose TPUs vs GPUs
TPUs work best for specific workloads. GPUs remain better for others.
Use TPUs for:
- Large language models (>10B parameters)
- High-throughput batch inference
- TensorFlow and JAX workloads
- Training with large batch sizes
- Long-running production workloads
Use GPUs for:
- PyTorch workloads (better ecosystem support)
- Small batch inference (<32 requests)
- Models requiring FP64 precision
- Workloads needing CUDA libraries
- Experimentation and prototyping
Cost Optimization on GCP
GCP offers aggressive discounts for committed usage.
Committed Use Discounts
Commit to GCP and save up to 91%.
1-year commitments save 37% for most machine types. Compute-optimized instances save up to 55%.
3-year commitments save 55% typically. Spend-based commitments reach 91% savings for large deployments.
Flexible Committed Use Discounts pool usage across projects and regions. Commit at the organization level. Apply discounts wherever resources run.
Combine with per-second billing. You pay only for actual usage. No rounding to the hour. Savings compound.
Preemptible and Spot VMs
Preemptible VMs cost 80% less than regular pricing. Google can terminate them with 30 seconds notice. Spot VMs offer the same pricing with better availability.
Use Spot VMs for batch inference processing, model training with checkpointing, data preprocessing pipelines, and development environments. Implement checkpointing to save state every 5 minutes. When Google preempts your instance, restart from the checkpoint.
Autoscaling for Resource Efficiency
Right-size automatically with intelligent autoscaling.
Vertex AI endpoints scale based on CPU, memory, or request count. Set minimum and maximum instance counts. Define target utilization. Vertex AI handles the rest.
Cloud Run scales to zero automatically. First request triggers an instance. Idle time costs nothing. Perfect for unpredictable workloads.
GKE autoscaling operates at three levels:
- Horizontal Pod Autoscaler adjusts pod count
- Vertical Pod Autoscaler optimizes resource requests
- Cluster Autoscaler adds or removes nodes
All three work together. Your cluster perfectly matches workload requirements.
Storage Cost Management
Cloud Storage offers multiple storage classes.
Standard provides instant access. Use for active datasets and frequently accessed models.
Nearline costs 50% less than Standard. Minimum 30-day storage duration. Access costs apply. Good for models accessed weekly.
Coldline costs 75% less than Standard. Minimum 90-day storage. Use for backup and compliance retention.
Archive costs 90% less than Standard. Minimum 365-day storage. Retrieval takes hours. Perfect for long-term archival.
Lifecycle policies transition objects automatically. New models start in Standard. After 30 days without access, move to Nearline. After 90 days, move to Coldline. Zero manual management required.
Security and Compliance
Enterprise ML demands enterprise security.
Identity and Access Management
IAM provides fine-grained access control.
Predefined roles cover common scenarios:
roles/aiplatform.userdeploys modelsroles/aiplatform.viewermonitors deploymentsroles/ml.developermanages all ML resources
Custom roles define exact permissions. Grant only what each team needs. Nothing more.
Service accounts represent applications. They authenticate without storing credentials. Workload Identity Federation connects external identity providers.
Network Security
VPC Service Controls create security perimeters around sensitive resources. Data can't leave the perimeter accidentally. Perfect for regulated data.
Private Google Access lets VMs access Google services without public IPs. Traffic never touches the internet. Attack surface shrinks dramatically.
Cloud Armor protects against DDoS attacks. Rate limiting prevents abuse. WAF rules block common attack patterns.
from google.cloud import accesscontextmanager_v1
perimeter = accesscontextmanager_v1.ServicePerimeter()
perimeter.title = "ML Production Perimeter"
perimeter.status.resources = [
"projects/123456",
]
perimeter.status.restricted_services = [
"aiplatform.googleapis.com",
"storage.googleapis.com",
]
perimeter.status.access_levels = ["accessPolicies/123/accessLevels/trusted_ip"]
Data Encryption and Protection
All data encrypts at rest by default. Google-managed keys work out of the box. No configuration required.
Customer-managed encryption keys (CMEK) give you complete control. You create keys in Cloud KMS. Google uses your keys for encryption. You can revoke access anytime.
Client-side encryption protects data before it reaches Google. You manage keys entirely. Google never sees unencrypted data. Meets the strictest compliance requirements.
VPC Service Controls prevent data exfiltration. Even administrators can't copy data outside authorized perimeters. Audit logs track every access attempt.
Monitoring and Observability
Production models need production monitoring.
Cloud Monitoring Integration
Cloud Monitoring collects metrics automatically from Vertex AI, GKE, and Cloud Run.
Key metrics to track:
- Prediction latency (P50, P95, P99 percentiles)
- Requests per second
- Error rates by type
- Resource utilization (CPU, memory, GPU)
- Model serving capacity
Create dashboards for each deployed model. Monitor SLIs (Service Level Indicators). Alert when SLOs (Service Level Objectives) breach.
Uptime checks verify endpoint availability from multiple regions. Synthetic requests run continuously. You catch issues before users do.
Cloud Logging for Debugging
Cloud Logging captures structured logs from all GCP services.
Query logs with the Logging Query Language. Filter by severity. Search for errors. Analyze patterns.
resource.type="ml_model"
severity >= WARNING
jsonPayload.latency_ms > 1000
Log-based metrics create custom monitoring metrics from log patterns. Alert on application-specific conditions.
Error Reporting automatically groups similar errors. See the most common failures first. Stack traces help debug issues quickly.
Model Monitoring and Explainability
Vertex AI Model Monitoring detects skew and drift.
Training-serving skew identifies differences between training data and production inputs. This catches data pipeline bugs early.
Prediction drift tracks how model outputs change over time. Sudden changes indicate problems requiring investigation.
Feature attribution explains individual predictions. See which features influenced each result. Required for regulated industries.
Set up monitoring schedules. Hourly for critical models. Daily for standard production models. Weekly for stable, mature models.
from google.cloud import aiplatform
monitoring_config = aiplatform.ModelDeploymentMonitoringJob(
display_name="llm-drift-monitor",
endpoint=endpoint_name,
model_deployment_monitoring_objective_configs=[
{
"deployed_model_id": deployed_model_id,
"objective_config": {
"training_dataset": {
"gcs_source": "gs://bucket/training-data/*.jsonl"
},
"training_prediction_skew_detection_config": {
"skew_thresholds": {
"input_feature_1": 0.3,
"input_feature_2": 0.3,
}
}
}
}
],
model_deployment_monitoring_schedule_config={
"monitor_interval": "3600s" # Check hourly
}
)
monitoring_config.create()
Best Practices for Production
Learn from successful GCP deployments.
Use Managed Services When Possible
Vertex AI eliminates operational overhead. Google handles infrastructure, scaling, and monitoring.
Only drop to GKE when you need features Vertex AI doesn't provide:
- Custom networking configurations
- Specific Kubernetes features
- Complex multi-service deployments
- Hybrid cloud requirements
For most LLM deployments, Vertex AI suffices. The operational simplicity outweighs minor flexibility losses.
Implement Circuit Breakers and Optimize Images
Circuit breakers prevent cascading failures. When error rates exceed thresholds, stop sending requests and give unhealthy services time to recover. Implement with libraries like pybreaker or custom logic tracking failure counts and timeout periods.
Optimize container images for faster starts. Use distroless base images containing only your application and runtime dependencies. Multi-stage builds keep images small by copying only artifacts to the final stage. Layer caching speeds builds when you put rarely changing layers first.
Version Everything
Track every deployed artifact.
Tag container images with git commits and timestamps: gcr.io/project/model:abc123-20250107-143052
Version models in Vertex AI Model Registry. Add metadata: training date, dataset version, performance metrics.
Store training datasets in versioned Cloud Storage buckets. Object Versioning tracks every change automatically.
This enables perfect reproducibility. Replicate any historical deployment exactly.
Getting Started: Your First GCP Deployment
Deploy your first model in three weeks.
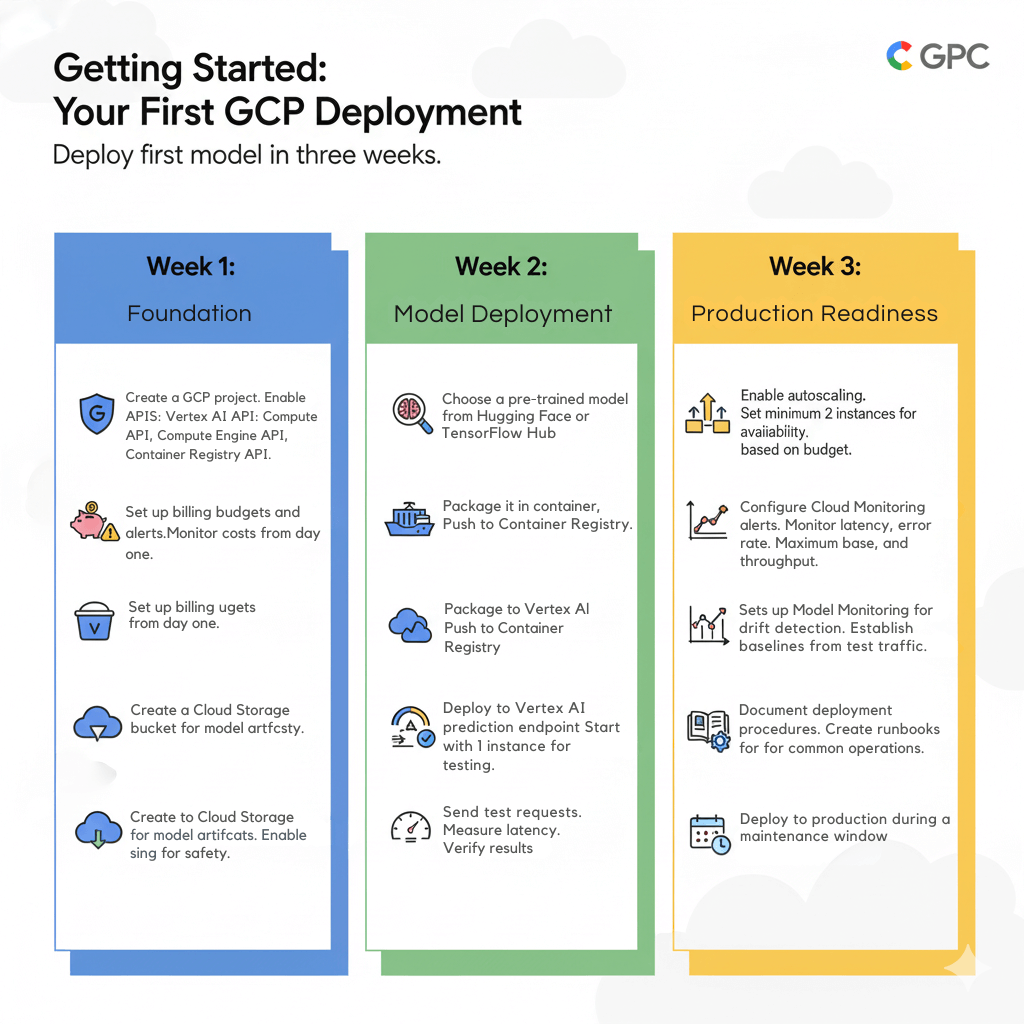
Week 1: Foundation
Create a GCP project. Enable required APIs:
- Vertex AI API
- Compute Engine API
- Cloud Storage API
- Container Registry API
Set up billing budgets and alerts. Monitor costs from day one.
Create a Cloud Storage bucket for model artifacts. Enable versioning for safety.
Week 2: Model Deployment
Choose a pre-trained model from Hugging Face or TensorFlow Hub.
Package it in a container. Push to Container Registry.
Deploy to Vertex AI prediction endpoint. Start with 1 instance for testing.
Send test requests. Measure latency. Verify results.
Week 3: Production Readiness
Enable autoscaling. Set minimum 2 instances for availability. Maximum based on budget.
Configure Cloud Monitoring alerts. Monitor latency, error rate, and throughput.
Set up Model Monitoring for drift detection. Establish baselines from test traffic.
Document deployment procedures. Create runbooks for common operations.
Deploy to production during a maintenance window.
Moving Forward with GCP Model Serving
GCP provides a mature ML infrastructure platform with clear advantages for production LLM deployments. TPU v5p delivers superior price-performance for large models. Vertex AI eliminates operational complexity through managed services. Cloud Run enables serverless inference for variable workloads.
Cost optimization reaches up to 91% through Committed Use Discounts and efficient resource management. The platform's sustainability focus supports ESG objectives while reducing operational costs. Native integration with Google's ML ecosystem accelerates development cycles.
Start with Vertex AI for managed deployment. Scale to GKE when you need custom configurations. Leverage TPUs for maximum throughput on large models. Monitor costs continuously and right-size resources based on actual usage patterns.
Frequently Asked Questions
What's the real cost difference between TPUs and GPUs on GCP?
TPU pricing depends on the generation and configuration. TPU v5p costs $4.20 per chip hour, and many teams leverage startup cloud consulting to evaluate whether this investment aligns with their growth stage and workload needs. A pod with 256 chips costs $1,075 per hour.
For comparison, an A100 40GB GPU costs $3.67 per hour. Eight A100 GPUs cost $29.36 per hour - similar capability to a small TPU pod slice.
For large models with high throughput requirements, TPUs deliver 40-60% better price-performance. For smaller models or PyTorch workloads, GPUs often cost less total.
Run benchmarks with your actual workload. Measure throughput and latency on both. Calculate cost per 1000 inferences. Pick the option that meets your SLA at lowest cost.
Can I deploy PyTorch models on Vertex AI?
Yes. Vertex AI supports PyTorch through custom containers.
Package your PyTorch model in a Docker container. Implement the prediction interface Vertex AI expects. Deploy like any other model.
Performance matches self-managed GKE deployments. You gain Vertex AI's monitoring and management features.
For maximum PyTorch performance, consider GKE with GPU nodes. You get direct access to CUDA and can optimize exactly as needed.
How does GCP handle multi-region deployment for LLMs?
GCP doesn't provide automatic multi-region failover for Vertex AI endpoints. You build this yourself.
Deploy separate endpoints in each region. Use Cloud Load Balancing to route requests. Configure health checks and failover policies.
Cloud CDN caches responses when appropriate. External HTTP(S) Load Balancer routes to the nearest healthy backend.
For stateful applications, use Cloud Spanner or Firestore for globally distributed data. Both replicate data automatically across regions.
Budget 20-30% more for multi-region versus single-region deployment. Complexity increases significantly. Only implement if your SLA requires it.
What's the best option for deploying small models (<7B parameters)?
Cloud Run provides the best economics for small models with intermittent traffic.
Quantize your model to 4-bit precision. This typically reduces size from 28GB to 7GB for a 7B parameter model. Fits easily in Cloud Run's memory limits.
Use the latest generation execution environment. Enable CPU boost for faster cold starts. Configure minimum instances to 0.
For steady traffic above 100 requests per minute, consider Vertex AI prediction endpoints instead. The always-on cost becomes lower than per-request pricing.
Does GCP offer GPU instances comparable to AWS P5 or Azure ND96?
GCP offers A2 Ultra instances with NVIDIA A100 80GB GPUs. Each a2-ultragpu-1g instance provides 1 GPU with 12 vCPUs and 170GB RAM.
For multi-GPU workloads, a2-ultragpu-8g provides 8 A100 GPUs per instance. This compares to AWS p4d.24xlarge or Azure ND96amsr_A100_v4.
GCP doesn't currently offer H100 instances in general availability. These remain in private preview for select customers.
For the absolute latest hardware, AWS tends to move fastest. For mature, stable GPU infrastructure, all three clouds offer comparable options.