Run LLM Inference Directly from BigQuery
Integrate Vertex AI LLMs with BigQuery for SQL-based inference, enabling petabyte-scale text processing without data movement or complex pipelines.

TLDR;
- ML.GENERATE_TEXT enables LLM inference directly from SQL without data movement
- Process millions of rows for sentiment analysis, classification, or text generation
- Automatic 24-hour result caching reduces costs for repeated queries
- Total costs for 1M inferences: ~$655 ($5 BigQuery + $650 Vertex AI endpoint)
Introduction
BigQuery ML bridges data warehousing and machine learning by enabling SQL-native model inference. Instead of exporting terabytes of data to separate ML platforms, call Vertex AI LLM endpoints directly from SQL queries. Process millions of customer reviews for sentiment analysis, generate product descriptions from catalog data, or extract entities from support tickets using standard SELECT statements with ML.GENERATE_TEXT functions.
This integration eliminates ETL complexity and data duplication costs. Data stays in BigQuery where analysts already work, security policies remain enforced, and query results cache automatically for 24 hours. BigQuery's petabyte-scale processing handles batch inference across entire datasets in minutes rather than hours, distributing LLM calls across Vertex AI endpoints automatically.
This guide covers BigQuery ML setup with Vertex AI connections, SQL-based inference patterns for text generation and classification, embedding generation for semantic search, cost optimization through result caching and partitioning, and monitoring workflows. You'll learn to process text at scale without leaving SQL, optimize costs through smart batching and caching strategies, and build production data pipelines that combine analytics with LLM capabilities. These patterns enable data teams to leverage LLMs without Python expertise or infrastructure management.
Architecture and Setup
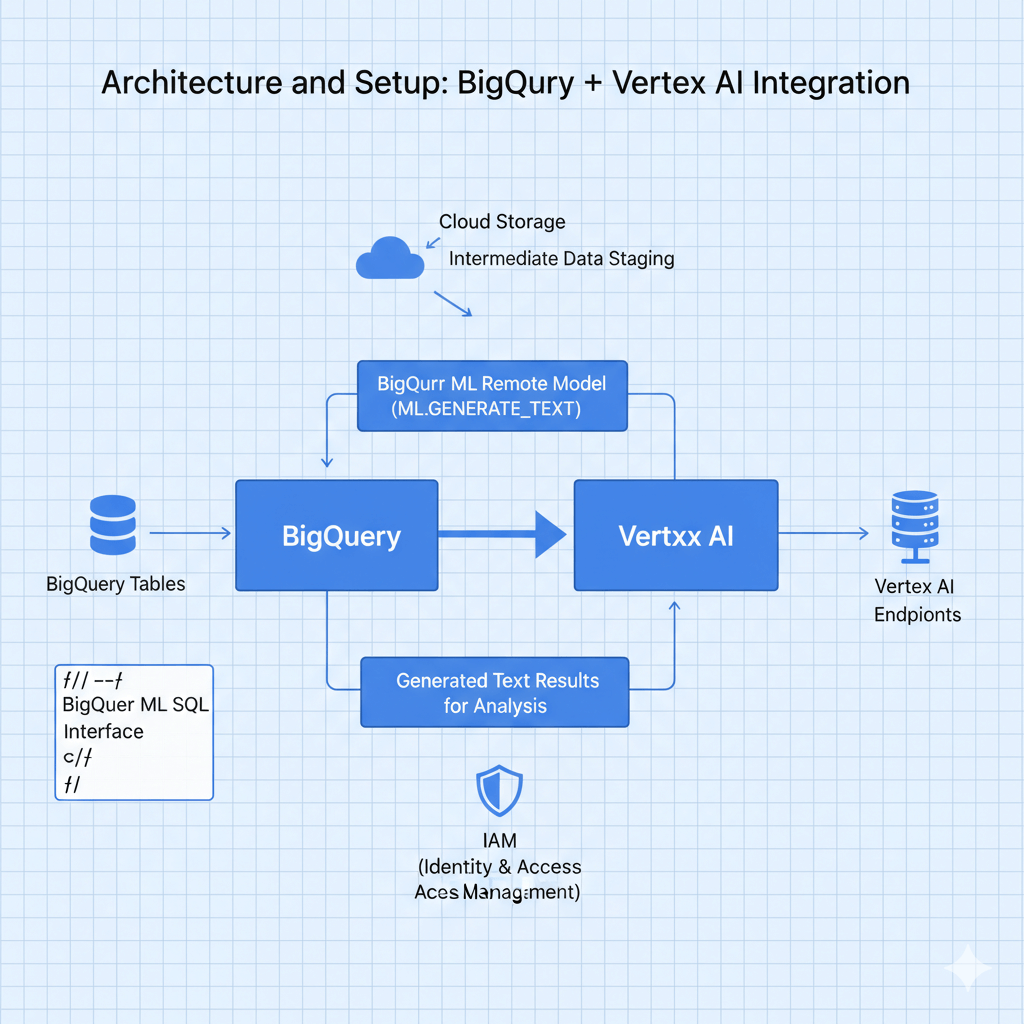
BigQuery connects to Vertex AI through BigQuery ML remote models. Data flows: query BigQuery tables, call Vertex AI endpoints via ML.GENERATE_TEXT SQL functions, results return to BigQuery for further analysis. IAM controls access, Cloud Storage stages intermediate data, and BigQuery ML provides the SQL interface.
Setup and Configuration
Connect BigQuery to Vertex AI.
Enable Required APIs
# Enable services
gcloud services enable \
bigquery.googleapis.com \
aiplatform.googleapis.com \
bigqueryconnection.googleapis.com
# Create service account
gcloud iam service-accounts create bq-vertex-sa \
--display-name="BigQuery Vertex AI Integration"
# Grant permissions
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding PROJECT_ID \
--member="serviceAccount:bq-vertex-sa@PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role="roles/aiplatform.user"
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding PROJECT_ID \
--member="serviceAccount:bq-vertex-sa@PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role="roles/bigquery.dataEditor"
Create BigQuery Connection
# Create connection to Vertex AI
bq mk --connection \
--location=us \
--project_id=PROJECT_ID \
--connection_type=CLOUD_RESOURCE \
vertex_ai_connection
Create Remote Model
-- Create reference to Vertex AI endpoint
CREATE OR REPLACE MODEL `project.dataset.llama_model`
REMOTE WITH CONNECTION `project.us.vertex_ai_connection`
OPTIONS (
endpoint = 'projects/PROJECT_ID/locations/us-central1/endpoints/ENDPOINT_ID'
);
SQL-Based Inference
Call LLM models from SQL.
Text Generation
-- Generate product descriptions
SELECT
product_id,
product_name,
ML.GENERATE_TEXT(
MODEL `project.dataset.llama_model`,
(SELECT CONCAT(
'Write a compelling product description for: ',
product_name,
'. Features: ',
features
) AS prompt),
STRUCT(
512 AS max_output_tokens,
0.7 AS temperature,
0.95 AS top_p,
TRUE AS flatten_json_output
)
) AS generated_description
FROM
`project.dataset.products`
WHERE
description IS NULL
LIMIT 100;
Sentiment Analysis at Scale
-- Analyze sentiment for millions of reviews
CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE `project.dataset.review_sentiment` AS
SELECT
review_id,
customer_id,
review_text,
ML.GENERATE_TEXT(
MODEL `project.dataset.llama_model`,
(SELECT CONCAT(
'Analyze the sentiment of this review and respond with only: Positive, Negative, or Neutral. Review: ',
review_text
) AS prompt),
STRUCT(
10 AS max_output_tokens,
0.1 AS temperature
)
) AS sentiment,
rating
FROM
`project.dataset.customer_reviews`
WHERE
DATE(created_at) = CURRENT_DATE();
-- Aggregate results
SELECT
sentiment,
AVG(rating) as avg_rating,
COUNT(*) as review_count
FROM
`project.dataset.review_sentiment`
GROUP BY
sentiment;
Batch Classification
-- Classify support tickets
CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE `project.dataset.ticket_categories` AS
SELECT
ticket_id,
subject,
description,
ML.GENERATE_TEXT(
MODEL `project.dataset.llama_model`,
(SELECT CONCAT(
'Classify this support ticket into one category: Technical, Billing, Account, or Feature Request. ',
'Subject: ', subject, '. ',
'Description: ', description
) AS prompt),
STRUCT(
20 AS max_output_tokens,
0.2 AS temperature
)
) AS category,
created_at
FROM
`project.dataset.support_tickets`
WHERE
category IS NULL
AND DATE(created_at) >= DATE_SUB(CURRENT_DATE(), INTERVAL 7 DAY);
Embeddings for Semantic Search
Generate and query text embeddings.
Create Embedding Model
-- Create embedding model reference
CREATE OR REPLACE MODEL `project.dataset.text_embedding_model`
REMOTE WITH CONNECTION `project.us.vertex_ai_connection`
OPTIONS (
endpoint = 'projects/PROJECT_ID/locations/us-central1/publishers/google/models/textembedding-gecko@003'
);
Generate Embeddings
-- Generate embeddings for documents
CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE `project.dataset.document_embeddings` AS
SELECT
document_id,
content,
ml_generate_embedding_result AS embedding
FROM
ML.GENERATE_EMBEDDING(
MODEL `project.dataset.text_embedding_model`,
(SELECT document_id, content FROM `project.dataset.documents`),
STRUCT(TRUE AS flatten_json_output)
);
Semantic Search
-- Find similar documents
WITH query_embedding AS (
SELECT ml_generate_embedding_result AS embedding
FROM ML.GENERATE_EMBEDDING(
MODEL `project.dataset.text_embedding_model`,
(SELECT 'machine learning deployment best practices' AS content),
STRUCT(TRUE AS flatten_json_output)
)
)
SELECT
d.document_id,
d.content,
-- Cosine similarity
(
SELECT SUM(a * b) / (
SQRT(SUM(a * a)) * SQRT(SUM(b * b))
)
FROM UNNEST(d.embedding) AS a WITH OFFSET pos_a
JOIN UNNEST(q.embedding) AS b WITH OFFSET pos_b
ON pos_a = pos_b
) AS similarity_score
FROM
`project.dataset.document_embeddings` d,
query_embedding q
ORDER BY
similarity_score DESC
LIMIT 10;
Cost Optimization
Reduce BigQuery ML costs.
Query Result Caching
-- Enable caching (automatic for most queries)
SELECT
/*+ OPTIONS(use_cache=true) */
product_id,
ML.GENERATE_TEXT(
MODEL `project.dataset.llama_model`,
(SELECT prompt FROM queries WHERE product_id = p.product_id)
) AS result
FROM
`project.dataset.products` p;
-- Cache results in table
CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE `project.dataset.cached_results`
PARTITION BY DATE(processed_date)
CLUSTER BY category
AS
SELECT
*,
CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() AS processed_date
FROM
ML.GENERATE_TEXT(...);
Batch Processing
Process large datasets in batches using LIMIT and OFFSET within WHILE loops. Set batch_size to 10,000 rows, iterate through dataset, and insert results to destination table between iterations to manage memory and avoid timeouts.
Materialized Views
-- Create materialized view for frequent queries
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW `project.dataset.daily_sentiment`
PARTITION BY DATE(analysis_date)
AS
SELECT
DATE(created_at) as analysis_date,
category,
AVG(sentiment_score) as avg_sentiment,
COUNT(*) as review_count
FROM
`project.dataset.review_sentiment`
GROUP BY
analysis_date, category;
-- Query materialized view (much cheaper)
SELECT * FROM `project.dataset.daily_sentiment`
WHERE analysis_date >= DATE_SUB(CURRENT_DATE(), INTERVAL 30 DAY);
Advanced Workflows
Complex data and ML pipelines.
Multi-Stage Processing
Build pipelines with multiple steps: extract entities using ML.GENERATE_TEXT with JSON output format, parse JSON results with JSON_EXTRACT_SCALAR, and analyze structured data with standard SQL aggregations.
Scheduled Inference
Use bq query --schedule='every 24 hours' to automate daily inference jobs. Process new data incrementally with WHERE clauses filtering by date or ID ranges.
Monitoring and Observability
Track BigQuery ML performance.
Query Monitoring
-- Monitor inference costs
SELECT
creation_time,
job_id,
user_email,
total_bytes_processed,
total_slot_ms,
ROUND(total_bytes_processed / POW(10, 12), 2) AS tb_processed,
ROUND((total_bytes_processed / POW(10, 12)) * 6.25, 2) AS estimated_cost_usd
FROM
`project.region-us.INFORMATION_SCHEMA.JOBS_BY_PROJECT`
WHERE
DATE(creation_time) = CURRENT_DATE()
AND statement_type = 'SELECT'
AND REGEXP_CONTAINS(query, r'ML\.GENERATE_TEXT')
ORDER BY
total_bytes_processed DESC
LIMIT 100;
Performance Analysis
-- Analyze ML model performance
SELECT
DATE(creation_time) as date,
COUNT(*) as query_count,
AVG(total_slot_ms) / 1000 as avg_execution_seconds,
SUM(total_bytes_processed) / POW(10, 9) as total_gb_processed
FROM
`project.region-us.INFORMATION_SCHEMA.JOBS_BY_PROJECT`
WHERE
creation_time >= TIMESTAMP_SUB(CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(), INTERVAL 7 DAY)
AND REGEXP_CONTAINS(query, r'llama_model')
GROUP BY
date
ORDER BY
date DESC;
Conclusion
BigQuery ML integration enables SQL-native LLM inference at petabyte scale without data movement or pipeline complexity. Data analysts leverage Vertex AI models using familiar SQL syntax, processing millions of rows for sentiment analysis, classification, or text generation in single queries. Automatic result caching and BigQuery's distributed architecture deliver cost-effective batch inference at scale.
Deploy BigQuery ML for workflows where data already resides in BigQuery and SQL expertise exceeds Python capabilities. Costs scale predictably: $6.25/TB for query processing plus Vertex AI endpoint charges. Optimize through result caching, partitioned tables, and scheduled off-peak processing. For 1M monthly inferences, expect ~$2,000 total costs ($0.625 query processing + $2,000 model calls).
Start with simple sentiment analysis or classification queries to validate integration, then expand to complex multi-stage pipelines combining embeddings, text generation, and entity extraction. BigQuery ML democratizes LLM access for data teams, eliminating infrastructure management while maintaining enterprise-grade security, compliance, and performance at scale.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does BigQuery ML pricing work for LLM inference?
BigQuery ML charges for bytes processed ($6.25/TB) plus Vertex AI endpoint charges. Processing 1M rows with 500-char prompts and 200-char responses costs: $5 BigQuery scan + $250 input + $400 output = $655 total. Optimize with LIMIT during development, enable result caching (90-day automatic), partition tables to reduce scans, and batch requests. BigQuery slots cost $0.04/slot-hour on-demand or use flat-rate reservations for predictable costs.
Can I fine-tune models through BigQuery ML?
Yes. BigQuery ML supports fine-tuning Vertex AI models directly via SQL. Create training table with prompt/response pairs, issue CREATE MODEL with REMOTE_MODEL_TYPE, BigQuery sends data to Vertex AI for tuning, tuned model becomes accessible via SQL. Costs: $50-200 for Vertex AI training plus BigQuery processing. This eliminates data movement security concerns.
How do I handle rate limits when processing millions of rows?
Use SELECT LIMIT during testing, TABLESAMPLE for representative subsets, partition processing with WHERE clauses on date/ID ranges, and request quota increases (default 60 requests/minute, can increase to 600-6000). Process overnight during low-traffic periods or use Dataflow for complex parallel processing with fine-grained rate control. Monitor quota usage in Cloud Console.