Deploy Mixtral 8x7B on Google Vertex AI
Deploy Mixtral 8x7B on Google Cloud Vertex AI for production inference. Leverage the mixture-of-experts architecture for cost-effective, scalable serving with 32K context windows.
TLDR;
- Mixtral's sparse MoE activates only 12.9B of 47B parameters, reducing costs 40-50% vs dense 70B models
- 3-year committed use discounts save 55% reducing monthly costs from $8,760 to $3,942
- GPTQ 4-bit quantization fits model on single A100 with <3% quality loss
- Blue-green deployments with traffic splitting enable zero-downtime updates
Introduction
Mixtral 8x7B revolutionizes LLM economics through sparse mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture. Unlike dense models that activate all parameters for every token, Mixtral activates only 2 of 8 expert networks per inference, processing 12.9B active parameters while maintaining 47B total capacity. This sparse activation delivers Llama 70B-class quality at 40-50% lower compute costs.
The model supports 32,768-token context windows, enabling document analysis, long-form content generation, and multi-turn conversations without truncation. Native multilingual training provides strong performance across English, French, German, Spanish, and Italian without language-specific fine-tuning. Vertex AI's managed infrastructure handles deployment complexity, auto-scaling, and load balancing automatically.
This guide covers Vertex AI deployment patterns, machine type selection, inference optimization with cost optimization strategies, auto-scaling configuration, vLLM and quantization. You'll learn to deploy Mixtral for both real-time and batch inference, implement blue-green deployments for safe updates, and optimize costs through committed use discounts and preemptible VMs. These patterns enable production-grade Mixtral serving at scale while maintaining sub-100ms latency and 99.9% availability.
Deployment Architecture and Options
Vertex AI provides two deployment patterns: managed online prediction for real-time inference and batch prediction for large-scale offline processing.
Managed Online Prediction
from google.cloud import aiplatform
# Initialize Vertex AI
aiplatform.init(
project="your-project-id",
location="us-central1",
staging_bucket="gs://your-bucket"
)
# Upload model to registry
model = aiplatform.Model.upload(
display_name="mixtral-8x7b",
artifact_uri="gs://your-bucket/models/mixtral-8x7b",
serving_container_image_uri="us-docker.pkg.dev/vertex-ai/prediction/pytorch-gpu.1-13:latest",
serving_container_environment_variables={
"MODEL_PATH": "/mnt/models/mixtral",
"TENSOR_PARALLEL_SIZE": "2"
}
)
# Deploy to endpoint
endpoint = model.deploy(
deployed_model_display_name="mixtral-deployment",
machine_type="n1-highmem-8",
accelerator_type="NVIDIA_TESLA_A100",
accelerator_count=2,
min_replica_count=1,
max_replica_count=10,
traffic_split={"0": 100}
)
print(f"Endpoint deployed: {endpoint.resource_name}")
Batch Prediction
For large-scale offline inference:
# Create batch prediction job
batch_prediction_job = model.batch_predict(
job_display_name="mixtral-batch-inference",
gcs_source="gs://your-bucket/input/prompts.jsonl",
gcs_destination_prefix="gs://your-bucket/output/",
machine_type="n1-highmem-16",
accelerator_type="NVIDIA_TESLA_A100",
accelerator_count=2,
starting_replica_count=5,
max_replica_count=20
)
# Monitor job
batch_prediction_job.wait()
print(f"Batch prediction complete: {batch_prediction_job.output_info}")
Machine Type Selection
Optimize cost and performance.
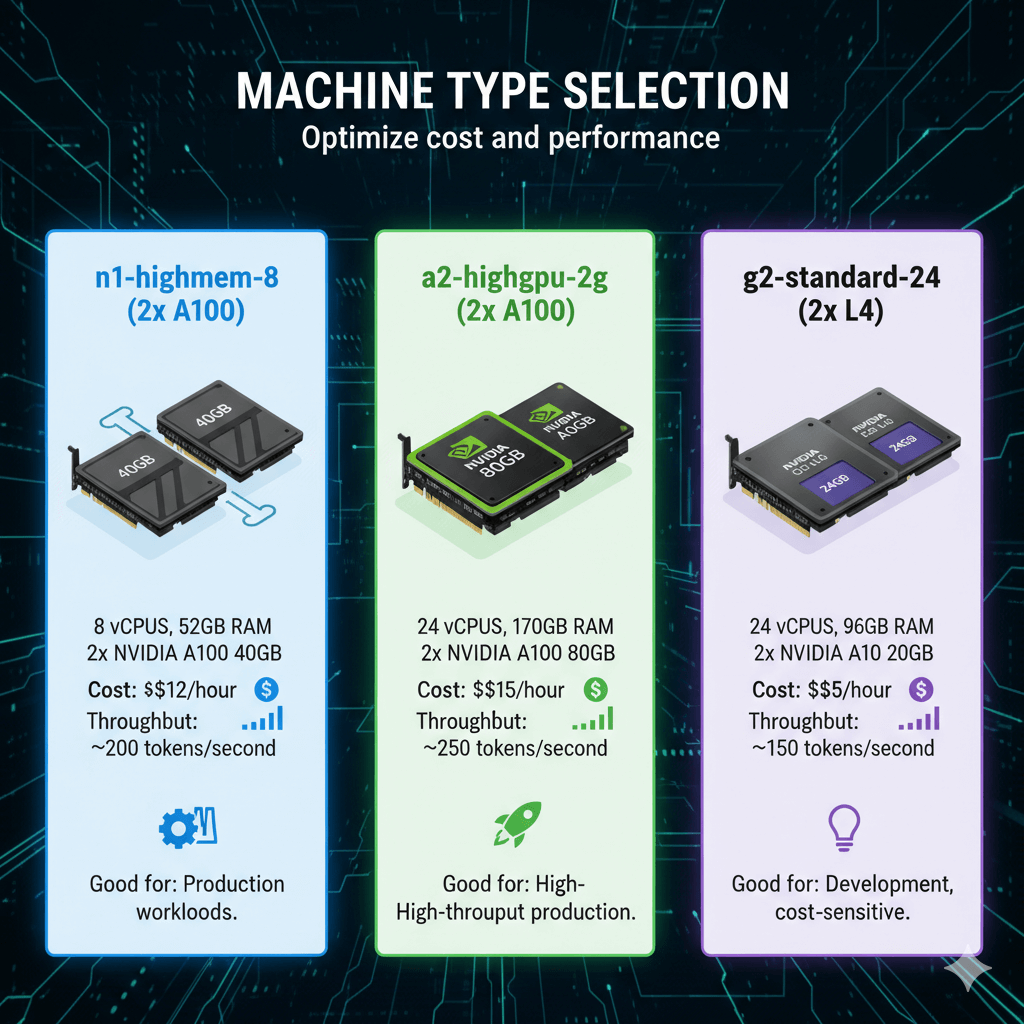
n1-highmem-8 (2x A100):
- 8 vCPUs, 52GB RAM
- 2x NVIDIA A100 40GB
- Cost: ~$12/hour
- Throughput: ~200 tokens/second
- Good for: Production workloads
a2-highgpu-2g (2x A100):
- 24 vCPUs, 170GB RAM
- 2x NVIDIA A100 80GB
- Cost: ~$15/hour
- Throughput: ~250 tokens/second
- Good for: High-throughput production
g2-standard-24 (2x L4):
- 24 vCPUs, 96GB RAM
- 2x NVIDIA L4 24GB
- Cost: ~$5/hour
- Throughput: ~150 tokens/second
- Good for: Development, cost-sensitive
Inference Optimization
Maximize throughput and reduce latency.
vLLM Integration
# Custom container with vLLM
# Dockerfile
FROM nvidia/cuda:12.1.0-runtime-ubuntu22.04
RUN pip install vllm transformers torch
COPY inference_server.py /app/
WORKDIR /app
EXPOSE 8080
CMD ["python", "inference_server.py"]
Inference server:
# inference_server.py
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
import uvicorn
app = FastAPI()
# Initialize vLLM
llm = LLM(
model="/mnt/models/mixtral",
tensor_parallel_size=2,
gpu_memory_utilization=0.95,
max_model_len=8192,
dtype="float16"
)
class InferenceRequest(BaseModel):
prompt: str
max_tokens: int = 512
temperature: float = 0.7
top_p: float = 0.95
@app.post("/predict")
async def predict(request: InferenceRequest):
sampling_params = SamplingParams(
temperature=request.temperature,
top_p=request.top_p,
max_tokens=request.max_tokens
)
outputs = llm.generate([request.prompt], sampling_params)
return {
"prediction": outputs[0].outputs[0].text,
"tokens_generated": len(outputs[0].outputs[0].token_ids)
}
@app.get("/health")
async def health():
return {"status": "healthy"}
if __name__ == "__main__":
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8080)
Quantization for Cost Savings
Deploy quantized model:
# Use GPTQ 4-bit quantized model
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, GPTQConfig
quantization_config = GPTQConfig(
bits=4,
dataset="c4",
group_size=128
)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"TheBloke/Mixtral-8x7B-Instruct-v0.1-GPTQ",
device_map="auto",
quantization_config=quantization_config
)
# Deploy to Vertex AI
model.save_pretrained("gs://your-bucket/models/mixtral-gptq")
Benefits:
- 75% memory reduction
- Fit on single A100 40GB
- 50% cost savings
- <3% quality loss
Auto-Scaling Configuration
Scale based on traffic patterns.
Configure Auto-Scaling
from google.cloud import aiplatform
# Update endpoint with auto-scaling
endpoint.update(
min_replica_count=2,
max_replica_count=20,
auto_scaling_target_utilization=70,
auto_scaling_metric_name="aiplatform.googleapis.com/prediction/online/accelerator/duty_cycle"
)
Traffic Splitting
Blue-green deployment:
# Deploy new version
new_deployment = model.deploy(
deployed_model_display_name="mixtral-v2",
endpoint=endpoint,
machine_type="n1-highmem-8",
accelerator_type="NVIDIA_TESLA_A100",
accelerator_count=2,
traffic_percentage=0 # Start with 0% traffic
)
# Gradual rollout
endpoint.update_traffic_split(traffic_split={
"mixtral-v1": 90,
"mixtral-v2": 10
})
# Monitor for 30 minutes, then complete rollout
endpoint.update_traffic_split(traffic_split={
"mixtral-v2": 100
})
# Undeploy old version
endpoint.undeploy(deployed_model_id="mixtral-v1")
Cost Optimization
Reduce Vertex AI spending.
Committed Use Discounts
Purchase committed use for predictable workloads:
# Calculate potential savings
gcloud compute commitments create mixtral-commitment \
--region=us-central1 \
--resources=count=2,type=NVIDIA_TESLA_A100 \
--plan=twelve-month
# Savings: 37% for 1-year, 55% for 3-year
Example savings (2x A100, 24/7):
- On-demand: $12/hour × 730 hours = $8,760/month
- 1-year CUD: $5,519/month (37% savings)
- 3-year CUD: $3,942/month (55% savings)
Preemptible VMs for Batch
Use preemptible for non-critical batch workloads:
# Batch prediction with preemptible VMs
batch_prediction_job = model.batch_predict(
job_display_name="mixtral-batch-preemptible",
gcs_source="gs://your-bucket/input/prompts.jsonl",
gcs_destination_prefix="gs://your-bucket/output/",
machine_type="n1-highmem-8",
accelerator_type="NVIDIA_TESLA_A100",
accelerator_count=2,
starting_replica_count=10,
max_replica_count=50,
# Enable preemptible VMs
model_parameters={"use_preemptible": True}
)
Savings: 60-80% vs on-demand
Right-Size Instances
Monitor utilization and adjust:
from google.cloud import monitoring_v3
# Query GPU utilization
client = monitoring_v3.MetricServiceClient()
query = """
fetch aiplatform.googleapis.com/Endpoint
| metric 'aiplatform.googleapis.com/prediction/online/accelerator/duty_cycle'
| group_by 1h, [value_duty_cycle_mean: mean(value.duty_cycle)]
| every 1h
"""
# If average utilization < 50%, consider smaller instances
# If average utilization > 85%, consider larger instances
Monitoring and Observability
Track performance with Cloud Operations.
Custom Metrics
from google.cloud import monitoring_v3
from google.api import metric_pb2 as ga_metric
# Create custom metric descriptor
client = monitoring_v3.MetricServiceClient()
project_name = f"projects/{project_id}"
descriptor = ga_metric.MetricDescriptor()
descriptor.type = "custom.googleapis.com/mixtral/tokens_generated"
descriptor.metric_kind = ga_metric.MetricDescriptor.MetricKind.GAUGE
descriptor.value_type = ga_metric.MetricDescriptor.ValueType.INT64
descriptor.description = "Number of tokens generated per request"
descriptor = client.create_metric_descriptor(
name=project_name,
metric_descriptor=descriptor
)
# Write metric
series = monitoring_v3.TimeSeries()
series.metric.type = "custom.googleapis.com/mixtral/tokens_generated"
series.resource.type = "generic_task"
series.resource.labels["project_id"] = project_id
series.resource.labels["location"] = "us-central1"
point = monitoring_v3.Point()
point.value.int64_value = 245 # tokens generated
point.interval.end_time.seconds = int(time.time())
series.points = [point]
client.create_time_series(name=project_name, time_series=[series])
Log-Based Metrics
# Create log-based metric for latency tracking
from google.cloud import logging_v2
client = logging_v2.MetricsServiceV2Client()
project_name = f"projects/{project_id}"
metric = {
"name": f"{project_name}/metrics/mixtral_latency",
"description": "Mixtral inference latency",
"filter": 'resource.type="aiplatform.googleapis.com/Endpoint" AND textPayload=~"latency:.*"',
"metric_descriptor": {
"metric_kind": "DELTA",
"value_type": "DISTRIBUTION",
"unit": "ms"
},
"value_extractor": 'EXTRACT(REGEXP_EXTRACT(textPayload, "latency:([0-9]+)"))'
}
client.create_log_metric(parent=project_name, metric=metric)
Conclusion
Mixtral 8x7B on Vertex AI delivers production-grade LLM inference with superior cost-performance. The sparse MoE architecture provides Llama 70B-class quality while activating only 12.9B parameters per token, reducing compute costs by 40-50% compared to dense alternatives. Vertex AI's managed infrastructure eliminates operational complexity while providing enterprise features like auto-scaling, traffic splitting, and integrated monitoring.
Deploy Mixtral on n1-highmem-8 with 2x A100 GPUs for $12/hour on-demand, or reduce costs by 37-55% through committed use discounts for predictable workloads. Use GPTQ 4-bit quantization to fit on single A100 instances, cutting costs in half with minimal quality loss. For variable traffic patterns, configure auto-scaling from 2 to 20 replicas to balance responsiveness and efficiency.
The combination of Mixtral's efficient architecture and Vertex AI's managed platform enables rapid deployment from prototype to production. Start with managed online prediction for real-time serving, add batch prediction for large-scale offline processing, and optimize continuously based on Cloud Monitoring metrics. This approach delivers sub-100ms P95 latency, 99.9% availability, and industry-leading cost efficiency for production LLM workloads.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does Mixtral's Mixture-of-Experts architecture affect deployment costs?
Mixtral 8x7B uses only 12.9B parameters per inference despite having 46.7B total parameters - only 2 of 8 expert networks activate per token. This dramatically reduces compute costs versus dense 70B models while achieving similar quality. On Vertex AI n1-standard-96 with 8x V100 GPUs, Mixtral 8x7B costs ~$18/hour versus $32/hour for dense 70B models on p4d instances (44% savings). Memory requirements (90GB) fit on 2x A100 40GB GPUs versus 4x needed for dense 70B, halving instance costs. However, MoE models have higher latency variance than dense models due to load imbalance across experts. Monitor active expert distribution via custom metrics - uneven activation (>70% requests hitting same 2 experts) indicates inefficient routing requiring re-tuning.
Can I serve Mixtral with higher throughput than dense models?
Yes, due to sparse activation. Mixtral achieves 1.8-2.2x higher throughput than Llama 2 70B on equivalent hardware because each forward pass computes fewer parameters. On 4x A100 GPUs with vLLM, Mixtral 8x7B serves 3200-3800 tokens/second versus Llama 2 70B at 1800-2200 tokens/second. The MoE architecture enables larger batch sizes (256 vs 128 for dense models) within same memory constraints. However, router network overhead adds 5-8% latency per token versus dense equivalents. For maximum throughput, tune --max-num-batched-tokens higher than dense models (32768 vs 16384) and enable expert parallelism if using tensor parallelism across GPUs. Monitor expert load balancing metrics to avoid stragglers.
Should I use Vertex AI Prediction or GKE for Mixtral deployment?
Choose Vertex AI Prediction for managed inference with built-in monitoring, auto-scaling, and A/B testing - ideal for teams without Kubernetes expertise or variable traffic patterns. Prediction costs ~$4.50/hour for n1-highmem-96 with 8 GPUs, provides automatic model versioning and canary deployments. Choose GKE for cost savings at scale (40-60% cheaper with committed use discounts), custom infrastructure requirements, or multi-model deployments sharing resources. GKE requires managing cluster, GPU drivers, and inference servers yourself but offers full control. For production workloads >1M requests/month, GKE's lower per-request costs and resource sharing justify operational complexity. For <500K requests/month or rapid experimentation, Vertex AI Prediction's convenience outweighs 40% cost premium.