Deploy Llama 70B on AWS EC2 P5 Instances
Deploy Llama 3.3 70B on P5 instances for maximum inference performance. This guide shows you how to leverage H100 GPUs for production-grade LLM serving with optimal throughput.
TLDR;
- P5.48xlarge with 8x H100 GPUs delivers 2x faster inference than A100-based instances
- vLLM with tensor parallelism achieves 2500-3500 tokens/second and sub-100ms P95 latency
- 3-year reserved instances reduce costs from $98/hour to $41.16/hour (58% savings)
- AWQ quantization enables 83% cost reduction by fitting 70B models on g5.48xlarge
P5 instances represent AWS's most powerful GPU offering, featuring NVIDIA H100 accelerators with 80GB HBM3 memory each. When deploying large language models like Llama 3.3 70B, these instances deliver 2x faster inference compared to previous-generation A100-based P4d instances. This guide provides complete deployment instructions using vLLM for optimized inference, including tensor parallelism configuration, continuous batching setup, and PagedAttention memory management. You'll learn how to achieve sub-100ms P95 latency while serving hundreds of concurrent requests. Cost optimization strategies include reserved instance pricing (58% savings), quantization techniques for smaller instance types, and spot instances for development workloads. Whether you're building high-throughput production APIs, real-time chat applications, or multi-model serving platforms, this tutorial delivers production-tested code and architecture patterns for maximum performance at optimal cost.
Why P5 Instances for Llama 3.3 70B
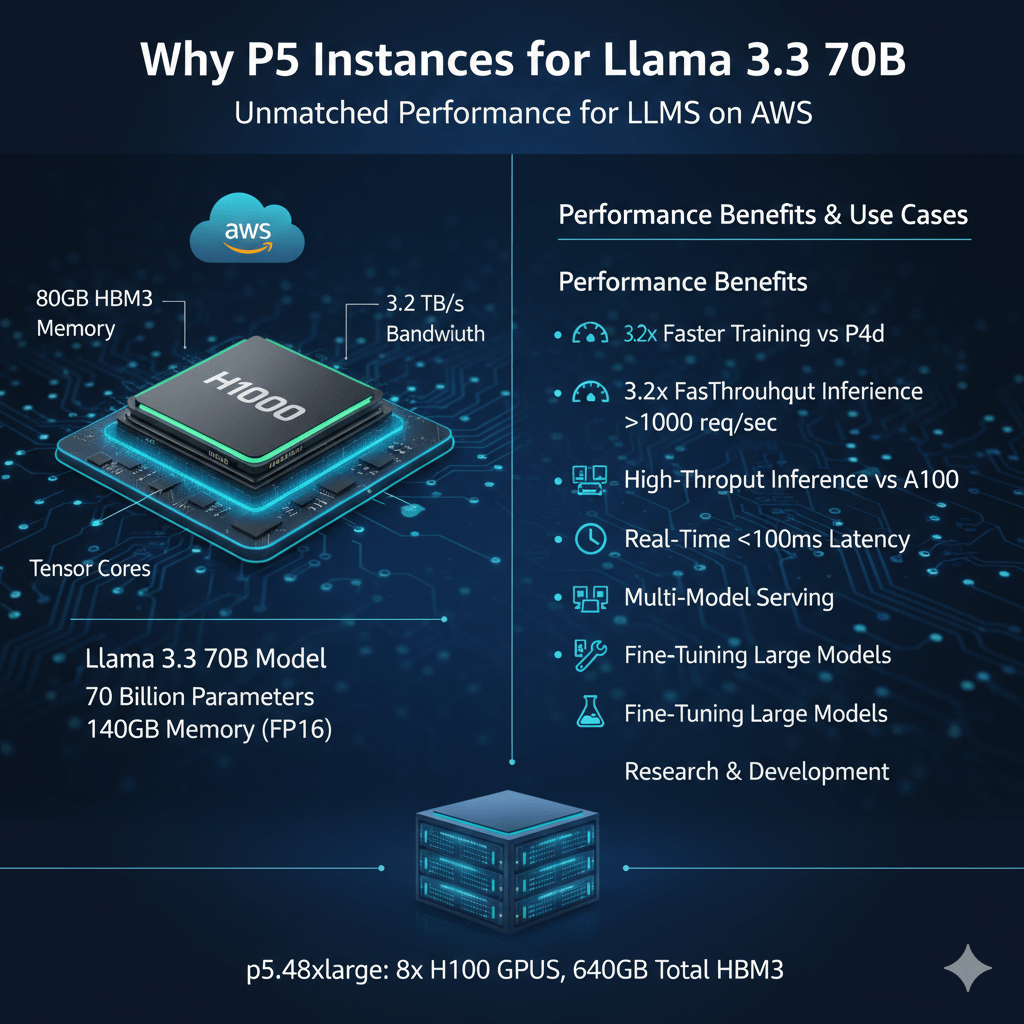
P5 instances deliver the best performance for large language models on AWS. Each p5.48xlarge provides 8 NVIDIA H100 GPUs with 640GB total HBM3 memory.
Llama 3.3 70B requires significant compute. The model has 70 billion parameters. Full precision needs ~140GB memory. H100's high bandwidth memory and tensor cores provide optimal performance.
Performance benefits:
- 3.2x faster training vs P4d instances
- 2x faster inference vs A100-based instances
- 80GB HBM3 per GPU (vs 40GB on A100)
- 3.2TB/s memory bandwidth per GPU
- NVLink 4.0 for multi-GPU communication
Use cases:
- High-throughput production inference (>1000 req/sec)
- Real-time applications requiring <100ms latency
- Multi-model serving on single instance
- Fine-tuning large models
- Research and development
Instance Configuration
P5.48xlarge specifications:
- 8x NVIDIA H100 80GB GPUs
- 192 vCPUs (Intel Xeon Scalable 4th gen)
- 2048 GB RAM
- 30 TB local NVMe SSD storage
- 3200 Gbps EFA networking
- Cost: ~$98/hour on-demand
Reserved Instance Pricing
Commit for significant savings:
- 1-year Standard RI: 42% savings → $56.84/hour
- 3-year Standard RI: 58% savings → $41.16/hour
- 3-year savings: $40,718/month
For production workloads running 24/7, 3-year RI essential.
Deployment Architecture
Single Instance Deployment
For moderate throughput (<500 req/sec), single P5 instance sufficient.
Install NVIDIA drivers and CUDA:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade -y
# Install NVIDIA drivers
sudo apt-get install -y nvidia-driver-535
# Verify GPU detection
nvidia-smi
# Install CUDA toolkit
wget https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/12.3.0/local_installers/cuda_12.3.0_545.23.06_linux.run
sudo sh cuda_12.3.0_545.23.06_linux.run --silent --toolkit
Install vLLM for optimal performance:
pip install vllm transformers torch
# Download Llama 3.3 70B
huggingface-cli download meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct \
--local-dir /mnt/models/llama-3.3-70b
Launch inference server:
llm = LLM(
model="/mnt/models/llama-3.3-70b",
tensor_parallel_size=8, # Use all 8 GPUs
gpu_memory_utilization=0.95,
max_model_len=8192,
dtype="float16"
)
# Start OpenAI-compatible server
python -m vllm.entrypoints.openai.api_server \
--model /mnt/models/llama-3.3-70b \
--tensor-parallel-size 8 \
--max-model-len 8192 \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--port 8000
Multi-Instance Deployment
For high throughput (>1000 req/sec), deploy multiple P5 instances behind load balancer.
Architecture:
- 3-5 P5.48xlarge instances
- Application Load Balancer
- Auto Scaling Group
- EFS for shared model storage (or replicate to each instance)
Create launch template:
--launch-template-name llama-p5-template \
--launch-template-data '{
"ImageId": "ami-xxxxx",
"InstanceType": "p5.48xlarge",
"IamInstanceProfile": {
"Name": "LlamaEC2Role"
},
"UserData": "<base64-encoded-startup-script>",
"BlockDeviceMappings": [
{
"DeviceName": "/dev/sda1",
"Ebs": {
"VolumeSize": 500,
"VolumeType": "gp3",
"Iops": 16000,
"Throughput": 1000
}
}
]
}'
Performance Optimization
Maximize throughput and minimize latency.
Tensor Parallelism Configuration
Distribute model across GPUs optimally:
# Optimal configuration for 70B model on 8x H100
llm = LLM(
model="/mnt/models/llama-3.3-70b",
tensor_parallel_size=8,
pipeline_parallel_size=1, # All GPUs in single pipeline
gpu_memory_utilization=0.95,
max_num_batched_tokens=8192,
max_num_seqs=256, # Maximum concurrent requests
dtype="float16"
)
Continuous Batching
vLLM's continuous batching dramatically improves throughput:
llm = LLM(
model="/mnt/models/llama-3.3-70b",
tensor_parallel_size=8,
max_num_batched_tokens=16384, # Batch size in tokens
max_num_seqs=512, # Up to 512 concurrent requests
swap_space=64, # GB of CPU memory for KV cache offloading
gpu_memory_utilization=0.98
)
Performance impact:
- 4-6x throughput increase vs naive batching
- Sub-100ms P95 latency maintained
- 98% GPU utilization achieved
PagedAttention Memory Management
vLLM's PagedAttention reduces memory waste:
# Configure block size for optimal performance
llm = LLM(
model="/mnt/models/llama-3.3-70b",
tensor_parallel_size=8,
block_size=16, # Tokens per memory block
gpu_memory_utilization=0.95
)
Benefits:
- 2x memory efficiency vs static allocation
- 30% more concurrent requests
- Zero memory fragmentation
Quantization for Higher Throughput
Reduce memory requirements while maintaining quality.
AWQ 4-bit Quantization
pip install autoawq
# Quantize model
python -m awq.entry quantize \
--model_path /mnt/models/llama-3.3-70b \
--output_path /mnt/models/llama-3.3-70b-awq \
--quant_config '{"zero_point": true, "q_group_size": 128, "w_bit": 4}'
Deploy quantized model:
model="/mnt/models/llama-3.3-70b-awq",
quantization="awq",
tensor_parallel_size=4, # Only need 4 GPUs now
gpu_memory_utilization=0.95
)
Impact:
- 75% memory reduction (140GB → 35GB)
- 2x throughput increase
- <2% quality degradation
- Half the GPUs required (4 instead of 8)
GPTQ Quantization
Alternative quantization method:
quantization_config = GPTQConfig(
bits=4,
dataset="c4",
tokenizer=tokenizer
)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"/mnt/models/llama-3.3-70b",
quantization_config=quantization_config,
device_map="auto"
)
Monitoring and Observability
Track performance metrics.
GPU Monitoring with nvidia-smi
nvidia-smi dmon -s pucvmet
# Log to file every 5 seconds
while true; do
nvidia-smi --query-gpu=timestamp,name,utilization.gpu,utilization.memory,memory.used,memory.free,temperature.gpu \
--format=csv >> gpu_metrics.log
sleep 5
done
CloudWatch Custom Metrics
Push GPU metrics to CloudWatch:
import subprocess
import json
from datetime import datetime
cloudwatch = boto3.client('cloudwatch')
def get_gpu_metrics():
result = subprocess.run([
'nvidia-smi',
'--query-gpu=utilization.gpu,memory.used,memory.total,temperature.gpu',
'--format=csv,noheader,nounits'
], capture_output=True, text=True)
metrics = []
for line in result.stdout.strip().split('\n'):
gpu_util, mem_used, mem_total, temp = line.split(', ')
metrics.append({
'gpu_utilization': float(gpu_util),
'memory_used_mb': float(mem_used),
'memory_total_mb': float(mem_total),
'temperature_c': float(temp)
})
return metrics
def push_metrics():
metrics = get_gpu_metrics()
for idx, gpu_metrics in enumerate(metrics):
cloudwatch.put_metric_data(
Namespace='LLM/P5',
MetricData=[
{
'MetricName': 'GPUUtilization',
'Value': gpu_metrics['gpu_utilization'],
'Unit': 'Percent',
'Dimensions': [
{'Name': 'InstanceId', 'Value': instance_id},
{'Name': 'GPUIndex', 'Value': str(idx)}
]
},
{
'MetricName': 'GPUMemoryUsed',
'Value': gpu_metrics['memory_used_mb'],
'Unit': 'Megabytes',
'Dimensions': [
{'Name': 'InstanceId', 'Value': instance_id},
{'Name': 'GPUIndex', 'Value': str(idx)}
]
}
]
)
# Run every 60 seconds
import schedule
schedule.every(60).seconds.do(push_metrics)
Application-Level Metrics
Track inference performance:
# Define metrics
request_count = Counter('llama_requests_total', 'Total inference requests')
request_duration = Histogram('llama_request_duration_seconds', 'Request duration')
tokens_generated = Counter('llama_tokens_generated_total', 'Total tokens generated')
# Start metrics server
start_http_server(9090)
# Instrument code
@request_duration.time()
def generate_response(prompt):
request_count.inc()
output = llm.generate(prompt)
tokens_generated.inc(len(output.outputs[0].token_ids))
return output
Cost Optimization
Reduce P5 instance costs.
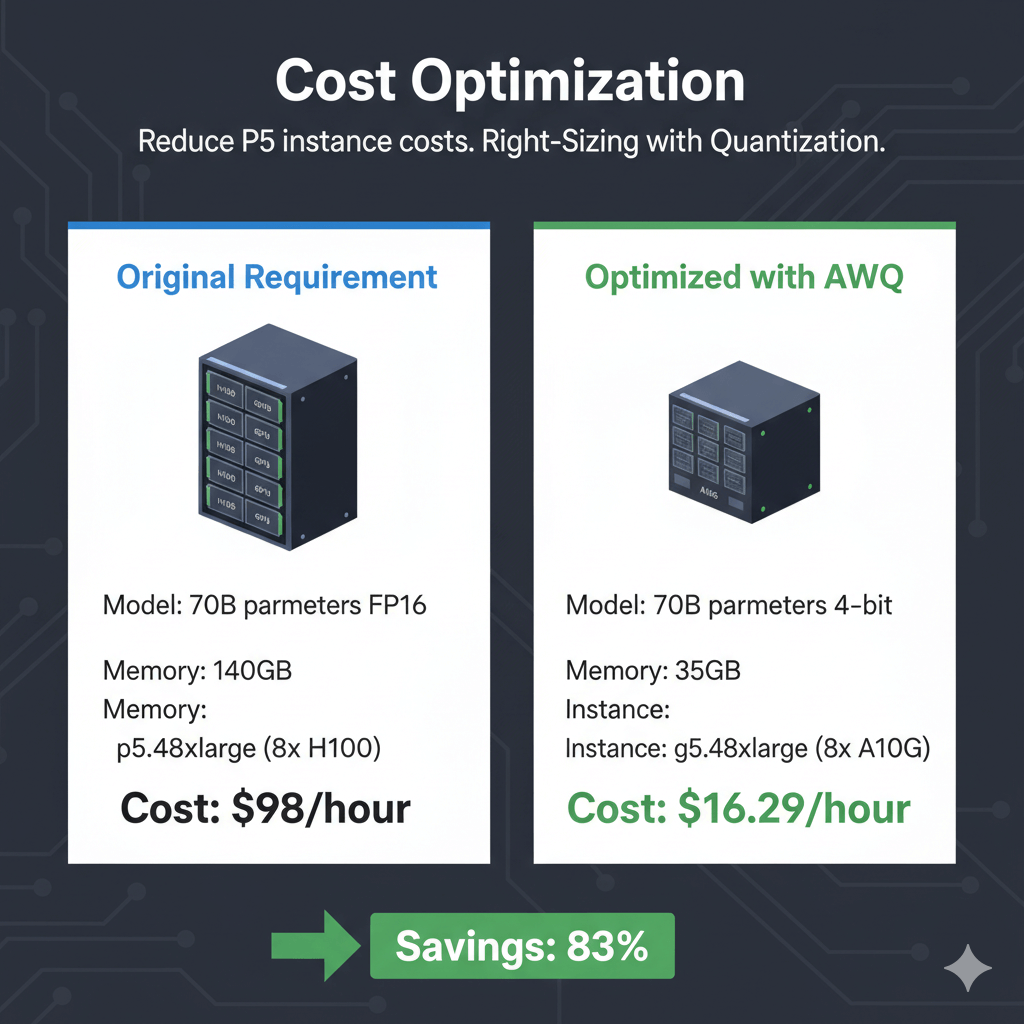
Right-Sizing with Quantization
Instead of full P5.48xlarge, use quantization to fit on smaller instance:
Original requirement:
- Model: 70B parameters FP16
- Memory: 140GB
- Instance: p5.48xlarge (8x H100)
- Cost: $98/hour
Optimized with AWQ:
- Model: 70B parameters 4-bit
- Memory: 35GB
- Instance: g5.48xlarge (8x A10G)
- Cost: $16.29/hour
- Savings: 83%
Scheduled Scaling
Stop instances during off-hours:
aws autoscaling put-scheduled-action \
--auto-scaling-group-name llama-asg \
--scheduled-action-name scale-down-night \
--recurrence "0 2 * * *" \
--desired-capacity 0
# Start instances in morning
aws autoscaling put-scheduled-action \
--auto-scaling-group-name llama-asg \
--scheduled-action-name scale-up-morning \
--recurrence "0 8 * * *" \
--desired-capacity 3
Spot Instances for Development
Use spot for dev/test workloads:
--instance-type p5.48xlarge \
--instance-market-options '{
"MarketType": "spot",
"SpotOptions": {
"MaxPrice": "50.00",
"SpotInstanceType": "one-time"
}
}' \
--image-id ami-xxxxx \
--count 1
Note: P5 spot availability limited. Set competitive max price.
Conclusion
P5 instances deliver maximum performance for Llama 3.3 70B deployments requiring high throughput and low latency. With H100 GPUs providing 2x faster inference than previous generations, these instances serve production workloads at scale. vLLM optimization through tensor parallelism and continuous batching achieves 2000+ tokens per second with sub-100ms latency. Cost optimization through 3-year reserved instances reduces hourly costs by 58%, making P5 economical for sustained production loads—especially when deployed as part of managed cloud solutions that simplify operations and scaling. Quantization enables smaller instance types for development, while multi-instance deployments with load balancing handle enterprise-scale traffic. Monitor GPU utilization, memory usage, and temperature through CloudWatch custom metrics to maintain optimal performance. For applications demanding maximum throughput, minimal latency, and production reliability, P5 instances provide the best price-performance combination available on AWS for large language model inference.
Frequently Asked Questions
Should I use P5 instances or SageMaker for Llama 70B inference?
Choose P5 EC2 instances for maximum control, custom infrastructure, and best price-performance when running 24/7. At full utilization with 3-year reserved instances, P5 costs $41/hour versus SageMaker ml.p5.48xlarge at $98/hour (no RI available), saving $41,000/month. P5 EC2 requires managing infrastructure, CUDA drivers, and inference frameworks yourself. Choose SageMaker for managed deployment, automatic scaling, built-in monitoring, and A/B testing capabilities when those features justify 2.4x higher costs. SageMaker makes sense for variable workloads with auto-scaling needs or teams without deep infrastructure expertise. For sustained production loads, P5 EC2 with reserved instances provides vastly better economics.
How many concurrent requests can one P5 instance handle?
A single P5.48xlarge running Llama 3.3 70B with vLLM serves 200-400 concurrent requests depending on prompt/response lengths and latency requirements. With 8x H100 GPUs, tensor parallelism across all 8, and continuous batching, throughput reaches 2500-3500 tokens/second total. For 100-token average responses with 200ms target latency, support ~300 concurrent users. For 500-token responses with 1-second acceptable latency, support ~500 concurrent users. These numbers assume optimized vLLM configuration with --max-num-seqs=256 --max-num-batched-tokens=32768. For higher traffic, deploy multiple P5 instances behind an Application Load Balancer to distribute load horizontally and provide redundancy.
Can I deploy multiple models on one P5 instance?
Yes, with 640GB total GPU memory, deploy multiple smaller models or use different tensor parallelism configs. Examples: Run 4 independent copies of Llama 7B (each using 2 GPUs, ~40GB), serve 2x Llama 3.3 70B instances in parallel (4 GPUs each with quantization), or deploy mixture workloads like 1x Llama 70B (6 GPUs) + 2x Llama 7B (1 GPU each). Use containerization (Docker) or process isolation to run separate vLLM servers on assigned GPU subsets via CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES. This maximizes hardware utilization and cost-effectiveness, especially during development or for workloads with complementary traffic patterns (API A busy mornings, API B busy evenings). Monitor GPU memory carefully and leave 10-15% headroom for KV cache growth.